
If you are looking for ways to preserve your future ability to become pregnant, and stop your biological clock, egg freezing (Oocyte cryopreservation or vitrification) may be for you.
Egg freezing is one of three forms of fertility treatment called Fertility preservation. Fertility preservation is the process of delaying conception that can be done with frozen eggs, sperm or embryos and is performed at our fertility clinic, Inovi Fertility & Genetics Institute.
In the cryopreservation process, your eggs are retrieved and then cooled to sub-zero temperatures to stop all biological activity, making them viable for your use in the future. Cryopreservation occurs with a process known as “vitrification”. This procedure involves the use of high concentrations of cryoprotectants to achieve the best protection of your unfertilized eggs for rapid cooling in liquid nitrogen. Vitrification allows for the cell to be preserved into a glass-like state. In slow or traditional egg freezing, ice crystals form in the egg which used to lower success rates so this method is no longer used.
WHY FREEZE MY EGGS?
You may consider egg freezing if you find yourself in one of these circumstances:
- Desire to save your eggs for future pregnancy or IVF treatment for social or career reasons called elective egg freezing
- Experiencing a chronic medical conditions which may damage your eggs or ovaries such as endometriosis, possibly interfering with future pregnancy
- Delaying pregnancy for medical reasons such as taking a medication that may be currently unsafe for pregnancy
- Undergoing cancer treatment such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy which damages egg supply
- At risk for early menopause, either by family history or low ovarian reserve testing as determined by blood tests (low AMH or high FSH) or ultrasound (low antral follicle count)
- Undergoing In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and prefer egg freezing to embryo freezing for religious or ethical reasons
ARE MY CHANCES OF A NORMAL PREGNANCY THE SAME AS WITH FRESH EGGS?
Good evidence exists that In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and ICSI after egg freezing (vitrification) and egg thawing has similar pregnancy rates or success rates compared to fresh egg (immediate) fertilization. Additionally there has been no evidence to date that this vitrification process increases the risks of chromosomal abnormalities, birth defects or developmental problems for your baby. Success rates, just as in IVF, are dependent on the age of the female partner at the time the egg freezing process takes place. The average age of women undergoing egg freezing is 37 years of age. However, success rates are higher when patients undergo egg freezing at age 35 or younger.
THE GOOD NEWS IS THAT YOU NOW HAVE OPTIONS!
If you choose to consider this path, your egg freezing is performed in “cycles,” each taking around 2 weeks from the day of ovarian stimulation until egg retrieval.
INOVI EGG FREEZING INCLUDES:
- Fertility Preservation Assessment
- Ovarian Stimulation and Monitoring
- Egg Retrieval & Egg Freezing
- One Year Egg Storage

GET STARTED WITH FERTILITY PRESERVATION
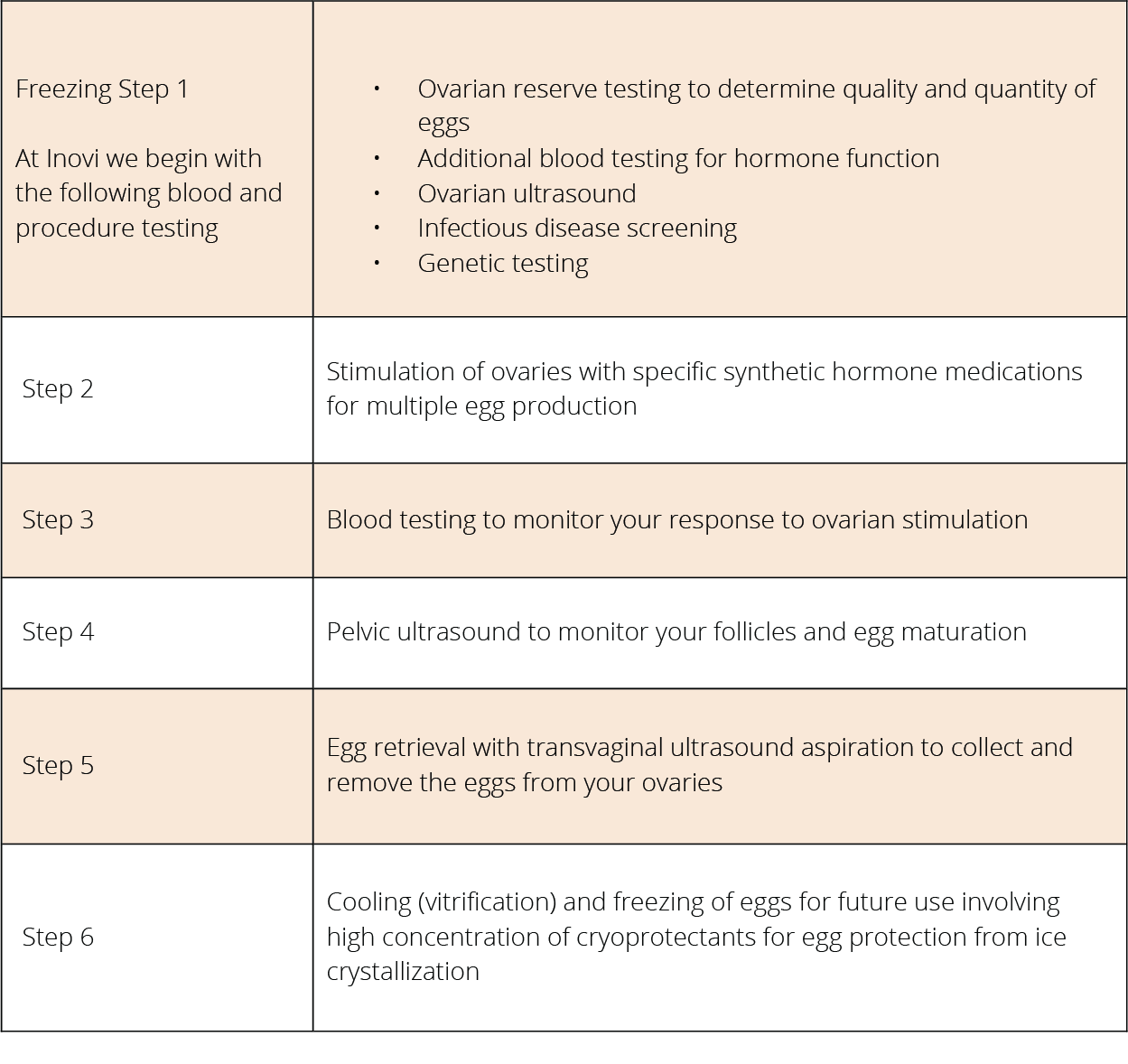
WHAT ARE EGG FREEZING STEPS
At Inovi Fertility & Genetics Institute, our fertility specialist will prescribe fertility medications (FSH and LH hormone injections), stimulating your ovaries for 9-12 days in the same way that is done in In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). During the stimulation, blood tests to measure your hormone levels and ultrasounds will be performed with the goal of getting 10 to 15 mature eggs for egg retrieval. The egg retrieval procedure is done the same way as in In Vitro Fertilization but the eggs are not fertilized by ICSI or traditional fertilization. Instead, your mature eggs will undergo the egg freezing process called oocyte cryopreservation. The most commonly used method is vitrification or “rapid freezing” in liquid nitrogen which prevents the formation of ice crystals in the eggs which can damage them.
Later on, when you are ready for pregnancy, our embryologists will assist in thawing and fertilizing your eggs by Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) using your partner’s or your chosen donor sperm. Once this is accomplished, the fertilized egg (embryo) will be implanted in your uterus in a procedure called embryo transfer. Success rates, also stated by the American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) as live birth rates, are similar to patients who are undergoing In Vitro Fertilization (“fresh cycle”).

If you are interested in learning more about the process of elective egg freezing or egg freezing for fertility preservation due to a medical condition or medical reason please contact us for a consultation with our fertility specialists.
Now you can relax and wait until you are ready for the next step toward fertility. This involves thawing of your eggs followed by fertilization with a healthy sperm and implantation in your uterus. If you are not a viable candidate for implantation, you may decide to use a gestational carrier.
At times, we may recommend the use of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). This process involves injecting a healthy sperm directly inside a mature egg which creates embryos which also can be cryopreserved.
FAQs

WHAT ARE MY CHANCES OF PREGNANCY AFTER IMPLANTATION?
Pregnancy rates after implantation average 30-60 percent depending on age. As your age increases, the rates decline. This makes it important for you and your spouse or partner to consider egg freezing as soon as you can.
Dr. Stephan Krotz and his fertility team are here to help you take the first steps in planning your initial visit to learn more about your choices for egg freezing and an exciting new future. We will be glad to discuss the cost of egg freezing as well as storage. If you need financing assistance we can provide that information for you.
Make certain you compare these statistics accurately across the age and demographic of each clinic patient’s base as many apply these differently when reporting. Both these factors influence the rates and outcomes as reported and found at the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology.
Post Related to Egg Freezing
How EMF Exposure May Influence Reproductive Health and Fertility

Key Takeaways As we learn more about EMF exposure and its effects on reproductive health, it’s more important than ever to stay informed. Electromagnetic fields (EMF) are ubiquitous, from the […]
Fertility Clinic: IVF, Egg Freezing & Expert Care Solutions

Did you know that about 1 in 8 couples struggle with infertility, often seeking reproductive healthcare, reproductive medicine, and assisted reproductive technology for support? A fertility clinic, an infertility practice […]
ES Fertility Treatments After Cancer: Essential Preservation Options

Cancer treatments can impact fertility and lead to future infertility, leaving many survivors with concerns about reproductive problems and ovarian cancers when starting a family, according to an oncofertility expert. […]
