Posted December 11, 2024 in Fertility Blog & Information
17 minute read
Understanding ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is crucial for anyone undergoing fertility treatments. This condition can turn the excitement of IVF into a nightmare. While some women experience mild symptoms of ovarian activity, others face severe complications like ovarian cysts and ovarian enlargement that require medical attention to cause. Recognizing the signs early can make all the difference.
Knowledge about OHSS empowers patients to advocate for their health. It’s not just about managing symptoms but also about making informed choices during treatment with injectable fertility medications, monitoring ovarian activity, and assessing ovarian blood vessels. Awareness helps in reducing risks and improving outcomes. The journey through fertility can be challenging, but understanding OHSS provides clarity and confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) can occur after fertility treatments, so understanding its symptoms is crucial for early detection.
- Recognize the different types of OHSS—mild, moderate, and severe—to better assess your condition and seek appropriate care.
- Monitor for symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and rapid weight gain, as these can indicate worsening OHSS.
- Be aware of risk factors like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and previous OHSS episodes to help prevent complications.
- Consult with healthcare providers for accurate diagnosis and explore various treatment options tailored to your situation.
- Always seek medical help if you experience severe symptoms or complications, as prompt intervention can be life-saving.
What is Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
Definition
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is a condition that occurs when the ovaries respond excessively to fertility medications. These medications stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. This overreaction can lead to serious complications.
Hormonal Imbalance
During fertility treatments, hormonal changes trigger ovarian activity. Medications like gonadotropins increase hormone levels. This leads to enlarged ovaries and the formation of ovarian cysts during fertility treatment. The ovaries become swollen due to fluid buildup. This fluid can leak into the abdominal cavity, causing discomfort and other issues.
Symptoms
Women with OHSS may experience various symptoms. Common signs include abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea. Some may also notice weight gain or shortness of breath. In severe cases, OHSS can lead to more serious health problems. These include blood clots or kidney failure. Understanding these symptoms can help patients seek timely treatment.
Diagnosis
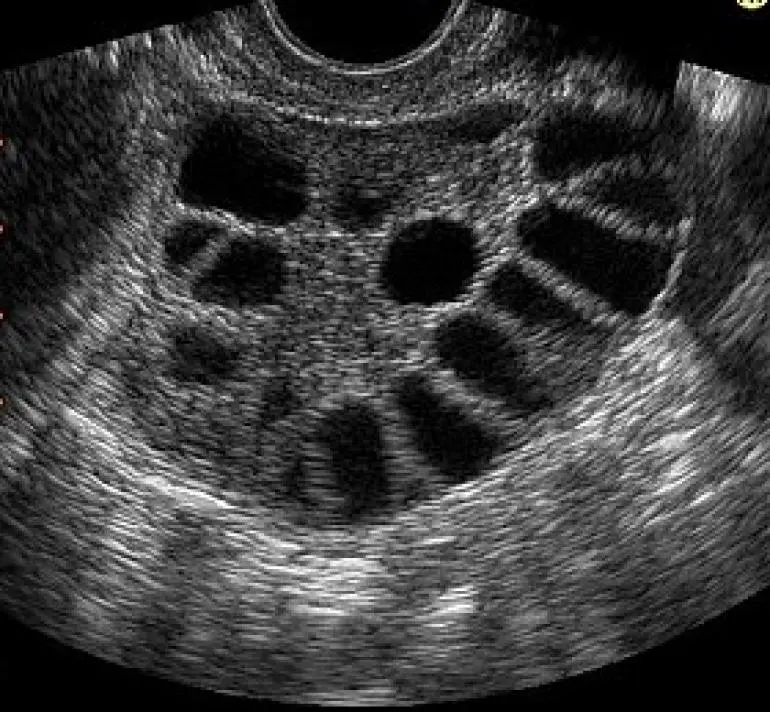
The diagnosis of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome typically involves a physical examination and medical history review. Doctors may conduct ultrasounds to check for enlarged ovaries and cysts. Blood tests can also evaluate hormone levels. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing OHSS. Women who are younger or have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are at higher risk. Those undergoing aggressive ovarian stimulation treatments may also face increased chances of OHSS. Awareness of these risk factors is essential for both patients and healthcare providers.
Importance of Understanding OHSS
Understanding ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is vital for women undergoing fertility therapies. Knowledge about potential risks helps in making informed decisions about treatment options. It empowers patients to recognize early symptoms and seek prompt medical care.
Healthcare providers play a key role in educating patients about OHSS. They should explain the signs, symptoms, and possible outcomes of this condition. Patients need clear information about their treatment plans and any associated risks.
Treatment Options
Management of OHSS focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Mild cases may require rest and monitoring at home. Severe cases may need hospitalization for intravenous fluids and medication adjustments. In some instances, procedures may be necessary to drain excess fluid from the abdomen.
Types of OHSS
Mild OHSS
Mild OHSS is the least severe form. Symptoms include mild abdominal discomfort, slight bloating, and some nausea. These symptoms usually resolve without treatment. Patients often do not require medical intervention. Monitoring is still important to ensure it does not progress.
Moderate OHSS
Moderate OHSS presents more noticeable symptoms. Patients may experience increased abdominal pain, significant bloating, and weight gain. Nausea can worsen, and vomiting might occur. Medical evaluation is necessary at this stage. Treatment may involve adjusting medications or monitoring fluid intake.
Severe OHSS
Severe OHSS involves serious complications. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, rapid weight gain, and difficulty breathing. Fluid accumulation in the abdomen can lead to distension. This condition requires immediate medical attention. Hospitalization may be necessary for proper management.
Treatment Approaches
The classification of OHSS greatly influences treatment options. Mild cases often require minimal intervention. Moderate cases need careful monitoring and possible medication adjustments. Severe cases necessitate aggressive treatment strategies. Doctors may use intravenous fluids or even drain excess fluid from the abdomen.
Risk of Progression
Monitoring is crucial as mild cases can progress to moderate or severe OHSS. Without proper observation, symptoms can worsen rapidly. For instance, a patient with mild discomfort may develop severe abdominal pain within days if untreated. Regular check-ups help in early detection of worsening symptoms.
Symptoms and Signs
Common Symptoms
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) presents various symptoms. Abdominal pain is one of the most common signs. Many women report feeling discomfort in their lower abdomen. This pain can range from mild to severe.
Bloating often accompanies abdominal pain. Women may feel a sense of fullness or swelling in their stomachs. This sensation can be uncomfortable and may lead to difficulty in wearing regular clothing.
Nausea is another frequent symptom. Some women experience feelings of sickness that can vary in intensity. These symptoms can make daily activities challenging.
Severity Escalation
Symptoms of OHSS can escalate quickly. In some cases, mild symptoms can worsen within days. Severe abdominal pain may develop, leading to increased discomfort.
Fluid retention is a key factor in this escalation. The body may accumulate excess fluid in the abdomen and other areas. This condition can result in significant weight gain over a short period.
Women may also notice changes in their urine output. Some may experience decreased urination, which indicates potential complications. Recognizing these changes is crucial for timely intervention.
Impact on Daily Life
The impact of OHSS symptoms on daily life can be profound. Routine tasks may become difficult due to discomfort and nausea. Work or school attendance might suffer as a result.
Emotional well-being can also be affected. Anxiety about health and pregnancy outcomes can increase during this time. Women may feel overwhelmed by their symptoms and uncertain about what to do next.
Seeking medical help becomes essential when symptoms worsen. Early recognition of signs allows for prompt treatment options. This proactive approach can help manage symptoms effectively and reduce complications.
Importance of Early Recognition
Recognizing early signs of OHSS is critical for effective management. Women should monitor their bodies closely after fertility treatments. Immediate reporting of symptoms like severe pain or rapid weight gain is vital.
Healthcare providers often recommend regular check-ups during treatment cycles. These appointments help identify any developing issues early on.
Timely intervention can prevent serious complications associated with OHSS. These include severe dehydration or blood clots, which pose risks to overall health.
Causes and Risk Factors
Hormonal Factors
Hormonal changes play a crucial role in the development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). The condition often arises from the use of fertility medications. These drugs stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. Increased levels of estrogen can lead to fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity.
High estrogen levels trigger a response in blood vessels. This response causes them to become more permeable. As a result, fluids leak into surrounding tissues. This process can lead to the swelling and discomfort associated with OHSS.
Specific Risk Factors
Certain conditions increase the risk of developing OHSS. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most significant factors. Women with PCOS often have many small cysts on their ovaries. They also tend to respond strongly to fertility treatments.
Age is another important factor. Younger women are at a higher risk for OHSS compared to older women. Studies show that women under 35 years old have a greater likelihood of experiencing severe symptoms.
Other risk factors include high body mass index (BMI) and a history of previous OHSS episodes. Women who have had OHSS before are more prone to developing it again.
Spontaneous Occurrence
Spontaneous OHSS can occur without any fertility treatments. This form is rare but possible. It happens when hormonal changes cause the ovaries to swell on their own. Certain medical conditions can trigger this response.
For example, some tumors can produce hormones that mimic those from fertility drugs. These tumors lead to increased estrogen levels, resulting in fluid buildup similar to that seen in treated patients.
Understanding these causes and risk factors is essential for prevention and management. Early identification can help healthcare providers monitor at-risk individuals closely during treatment.
Diagnosis Process
Physical Exams
Healthcare providers start the diagnosis of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) with physical examinations. They check for symptoms like abdominal swelling, pain, and tenderness. These signs can indicate fluid accumulation in the abdomen. The provider may also assess vital signs, including blood pressure and heart rate. Abnormal readings can signal complications related to OHSS.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging plays a critical role in diagnosing OHSS. Providers often use ultrasound to visualize the ovaries and assess their size. Enlarged ovaries are a common sign of OHSS. Ultrasound can also reveal fluid buildup in the abdomen or around the ovaries. This information helps confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of the condition.
Patient History
Patient history is essential in assessing the likelihood of OHSS. Providers ask about recent fertility treatments, such as hormone injections. A history of multiple egg retrievals increases the risk of developing OHSS. Understanding previous responses to fertility medications helps predict potential issues. Providers inquire about any past incidents of OHSS, as recurrence is possible.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is crucial for managing symptoms effectively. Recognizing OHSS early allows healthcare providers to implement treatment strategies sooner. This can prevent severe complications, such as dehydration or thrombosis. Patients experiencing mild symptoms may receive monitoring and supportive care. For those with moderate to severe symptoms, more aggressive interventions may be necessary.
Treatment Options
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of OHSS. In mild cases, rest and hydration may suffice. Moderate cases might require medication to reduce symptoms and prevent complications. Severe cases often necessitate hospitalization for close monitoring. Intravenous fluids may be administered to manage dehydration.
Monitoring Symptoms
Ongoing monitoring is vital during treatment for OHSS. Patients should report any worsening symptoms to their healthcare provider immediately. Symptoms like shortness of breath or severe abdominal pain require urgent attention. Regular follow-ups help ensure that treatment remains effective and any complications are addressed promptly.
Treatment Options
Severity Levels
Treatment for ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) varies based on its severity. In mild cases, observation is often sufficient. Patients may not require any specific treatment. Medical professionals monitor symptoms closely.
Moderate cases may need more attention. Patients might receive hormone treatments to help manage their symptoms. This can include adjusting the dosage of fertility medications. Severe cases, however, can lead to serious complications. Hospitalization is sometimes necessary for these patients. They require specialized care and monitoring.
Hydration Management
Hydration plays a key role in treating OHSS. Patients often experience fluid retention due to hormonal changes. Keeping well-hydrated helps reduce this retention. Water intake should be increased significantly.
Electrolyte management is also important. Electrolytes like sodium and potassium can become imbalanced during OHSS. Monitoring these levels helps prevent complications. Doctors may recommend electrolyte solutions to maintain balance.
Medications for Symptoms
In severe cases of OHSS, medications are critical for symptom relief. Certain fertility drugs help alleviate discomfort and reduce swelling. For instance, diuretics may be prescribed to help eliminate excess fluid from the body.
Other medications can target pain and inflammation. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used for pain relief. These can help manage discomfort without causing further hormonal imbalance.
Patients might also receive injectable fertility medications if they have not already done so during treatment cycles. Gonadotrophin administration is another method used in managing hormone levels effectively.
Prevention Strategies
Personalized Plans
Doctors should create personalized medication plans for patients at risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Each plan must consider individual health factors. These include age, hormone levels, and medical history. A tailored approach helps to minimize the risk of OHSS.
For instance, some women may require lower doses of fertility drugs. Others may benefit from different types of medications altogether. By adjusting treatment based on personal needs, healthcare providers can reduce the chances of complications like OHSS.
Monitoring Techniques
Regular monitoring is crucial during treatment cycles. This helps detect early signs of OHSS. Healthcare professionals often use blood tests and ultrasounds to track hormone levels and ovarian response.
Patients should be aware of their symptoms. Common signs include abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea. If these symptoms arise, immediate consultation with a doctor is essential. Early intervention can prevent severe cases of OHSS.
Alternative Approaches
Alternative strategies can also help prevent OHSS. One method is called “coasting.” This involves pausing hormone injections once sufficient follicles develop. This pause allows the body to stabilize before triggering ovulation.
Another option is freezing embryos instead of transferring them immediately. This allows time for the ovaries to recover after stimulation. Patients can then undergo a future transfer when they are in a better state.
These approaches have shown promise in reducing the incidence of OHSS. They give patients more control over their treatment outcomes while minimizing risks.
Risk Assessment
Assessing the risk factors for OHSS is vital. Factors such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Women with PCOS often respond strongly to fertility drugs, leading to overstimulation.
Doctors must educate patients about these risks. Understanding personal risk factors encourages proactive management during treatment cycles.
Patient Education
Educating patients about OHSS is essential for prevention. Knowledge empowers individuals to recognize symptoms early and seek help. Informational resources can include brochures or workshops offered by clinics.
Patients should feel comfortable asking questions about their treatment plan. Clear communication between doctors and patients fosters a collaborative approach to care.
Managing OHSS Complications
Fluid Accumulation
Fluid accumulation is a common complication of severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). This condition leads to excess fluid in the abdomen, known as ascites. Patients may experience abdominal swelling and discomfort. In some cases, this fluid can cause shortness of breath if it presses against the diaphragm.
Doctors often monitor patients closely for signs of fluid buildup. They may use ultrasound to assess the amount of fluid present. If necessary, they can perform a procedure called paracentesis. This involves inserting a needle into the abdomen to remove excess fluid. Such interventions help relieve symptoms and prevent further complications.
Blood Clots
Blood clots are another serious risk associated with severe OHSS. The increased hormone levels can lead to changes in blood flow and clotting factors. Patients may develop deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which occurs when a clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. Symptoms of DVT include swelling, pain, and redness in the affected leg.
Severe cases can lead to pulmonary embolism, where a clot travels to the lungs. This condition is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. Healthcare providers often recommend blood thinners for at-risk patients to reduce this risk.
Importance of Monitoring
Ongoing monitoring is crucial for patients experiencing severe symptoms of OHSS. Regular check-ups allow healthcare providers to detect complications early. They can assess vital signs and monitor laboratory results, such as electrolyte levels and kidney function.
Patients should report any new or worsening symptoms immediately. These may include severe abdominal pain, difficulty breathing, or leg swelling. Prompt reporting ensures timely intervention and reduces risks.
Management Strategies
Managing complications from OHSS involves several strategies to ensure patient safety. Here are some effective approaches:
- Hydration: Maintaining proper hydration helps manage fluid balance.
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe diuretics to help eliminate excess fluid.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Resting and avoiding strenuous activities can reduce strain on the body.
- Regular Check-Ups: Frequent visits help track progress and adjust treatment as needed.
When to Seek Medical Help
Severe Symptoms
Patients must be vigilant about their health during treatment for ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Severe symptoms can indicate a serious condition. Rapid weight gain, especially more than 2.2 pounds in a day, is alarming. This may signal fluid accumulation in the abdomen. Shortness of breath can also occur and may suggest fluid buildup around the lungs. Both symptoms require immediate medical attention.
Critical Warning Signs
Several critical warning signs should not be ignored. Abdominal pain that feels severe or persistent can indicate complications. Nausea and vomiting are also concerning if they become frequent. Changes in urine output can signal kidney issues, which can happen with OHSS. If any of these symptoms arise, contact a healthcare provider right away.
- Rapid weight gain
- Shortness of breath
- Severe abdominal pain
- Frequent nausea and vomiting
- Decreased urine output
Each of these signs can escalate quickly. Delaying care can lead to more serious complications. It is essential to take them seriously.
Communication Importance
Communication with healthcare providers is vital during treatment for OHSS. Patients should report any new or worsening symptoms immediately. Open dialogue helps doctors monitor the condition effectively. Regular check-ins allow for adjustments in treatment if necessary.
Doctors often rely on patient feedback to identify issues early. They may schedule follow-up appointments or recommend additional tests based on reported symptoms. Being proactive ensures better management of the condition.
Emergency Situations
In some cases, patients may face emergencies related to OHSS. These situations require urgent intervention from medical professionals. For instance, if swelling in the abdomen causes significant discomfort, it could lead to complications like torsion or rupture of ovarian cysts.
Patients should know when to call for help. If symptoms escalate quickly or become unbearable, seek emergency care immediately. Understanding personal limits is crucial in managing health effectively.
Final Remarks
Understanding ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is crucial for anyone undergoing fertility treatments. You’ve learned about its types, symptoms, causes, and how to manage it effectively. Recognizing the signs early can make a big difference in your health and well-being.
Stay informed and proactive. If you experience any symptoms or have concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Your health matters, and getting timely help can prevent complications. Keep this information handy and share it with others who might benefit from it. Together, we can navigate the complexities of OHSS and ensure a safer journey through fertility treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)?
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) is a condition that occurs when the ovaries become swollen and painful due to excessive stimulation, often from fertility treatments.
What are the types of OHSS?
There are two main types of OHSS: mild and severe. Mild cases usually resolve on their own, while severe cases can lead to serious complications and require medical intervention.
What are the common symptoms of OHSS?
Common symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and rapid weight gain. Severe cases may involve difficulty breathing and reduced urine output.
Who is at risk for developing OHSS?
Women undergoing fertility treatments, particularly those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), are at higher risk. Age and hormone levels also play a role.
How is OHSS diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, review of symptoms, and ultrasound imaging to assess ovarian size and fluid accumulation in the abdomen.
What treatment options are available for OHSS?
Treatment varies by severity. Mild cases may need rest and hydration, while severe cases might require hospitalization for monitoring and fluid management.
When should I seek medical help for OHSS?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe abdominal pain, difficulty breathing, or significant changes in urination. Early intervention can prevent complications.
