Posted February 08, 2025 in Fertility Blog & Information
13 minute read
Key Takeaways
- Adenomyosis can affect fertility by disrupting reproductive organs and complicating pregnancy outcomes. Having the ability to identify symptoms sooner can help reduce adenomyosis effects on fertility.
- Diagnosis is Key: A thorough medical history, physical exam, and imaging techniques are crucial for accurate diagnosis, which guides effective treatment plans and improves fertility outcomes.
- Implementing healthy lifestyle changes and a balanced diet can help manage adenomyosis symptoms and support fertility efforts.
- Medications, hormonal treatments, and surgical options, along with assisted reproductive technologies, offer pathways to manage adenomyosis and enhance fertility prospects.
- Non-Surgical and Surgical Treatments: Both approaches have distinct benefits and implications for fertility, requiring careful consideration and consultation with healthcare providers.
- Coping with adenomyosis involves emotional and psychological support, making support groups and counseling valuable resources for those affected.
Knowing how adenomyosis affects reproductive health is key. Adenomyosis, a condition in which endometrial tissue grows into the muscle of the uterus, has been linked to fertility issues and can be quite painful. By understanding adenomyosis red flags such as heavy periods and pelvic pain, people with the condition can get help before it’s too late.
Treatment options vary from medication to surgical procedures, bringing different benefits. Working closely with healthcare providers can help individuals and couples find the right balance between symptom relief and fertility goals. Tracking lifestyle changes like diet and stress management encourages a greater focus on wellness.
Keeping up with new developments in medical research offers more information on managing this emerging condition. By taking an informed and proactive approach, those living with adenomyosis can manage their symptoms with more confidence and clarity, improving their overall quality of life.
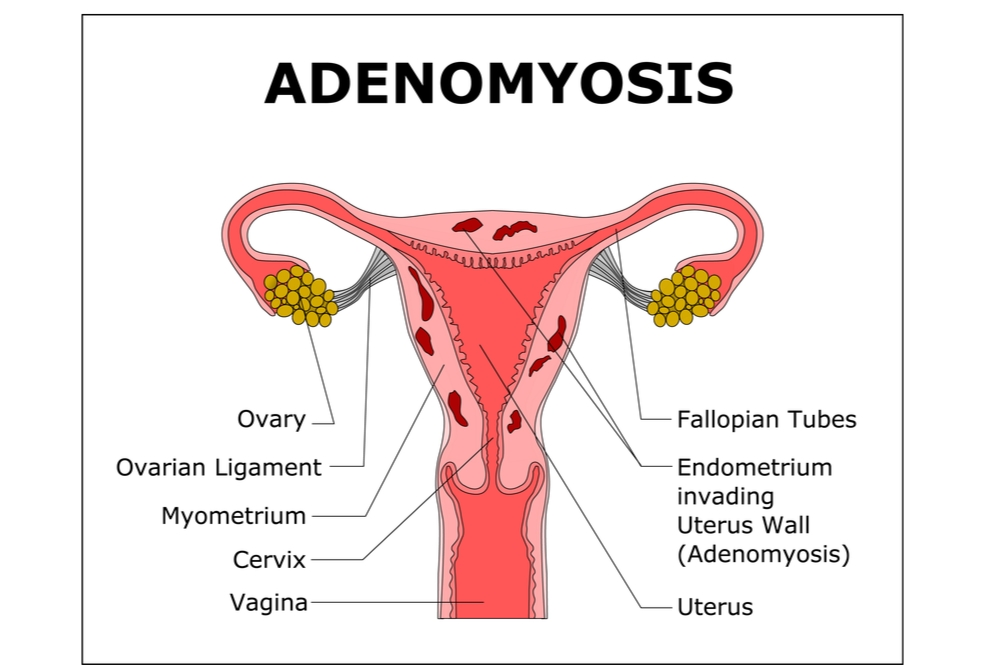
What is Adenomyosis
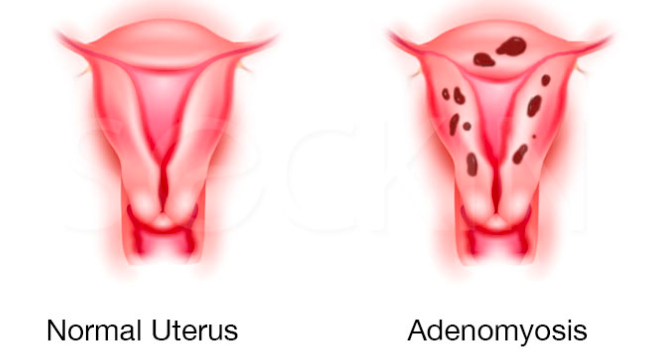
Adenomyosis is a common benign condition. It happens when the endometrial glands and stroma invade the myometrium or muscle layer of the uterus. These inflammatory tissues are located directly underneath the endometrial-myometrial junction.
They infiltrate the myometrium by intruding a minimum of 0.1 inches beneath the basal layer of the endometrium. This condition is surrounded by hyperplastic tissue, making it a special challenge for those afflicted. Despite being a common condition of reproductive aged women, adenomyosis is often underdiagnosed, with estimates ranging as low as 5-10% up to 70%.
Usually, adenomyosis affects women during their childbearing years, more commonly between the ages of 35 and 50. The majority of diagnoses are in women between the ages of 40 and 50, representing 70% to 80% of adenomyosis cases. Join us in learning more about adenomyosis symptoms, causes, and complications.
Symptoms of Adenomyosis
Women living with adenomyosis may face debilitating symptoms which impact their quality of life. The most typical symptoms are heavy menstrual periods, long periods and debilitating menstrual cramps.
Some may even experience pelvic pain or pressure. These symptoms range in severity and can often mimic fibroids or other conditions, complicating the diagnosis process.
Causes and Risk Factors
It’s not entirely clear what causes adenomyosis, though a few things can put you at risk. They include hormonal imbalances, previous uterine surgeries, and childbirth.
Genetics could be a factor, given that the condition is known to be familial.
Complications Linked to Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis may cause complications, most notably related to fertility. Studies show that assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are linked to a 50% reduced clinical pregnancy rate.
Further, these technologies contribute to increased miscarriage rates. Targeted interventions such as treatment with GnRH-a therapy prior to frozen embryo transfer in IVF have the potential to mitigate the harms.
How Adenomyosis Affects Fertility
Impact on Reproductive Organs
While adenomyosis cannot be deemed a directly reproductive issue, it can severely impact the reproductive organs, most notably the uterus. Women with adenomyosis may present with decreased expression of progesterone receptors within the endometrium and myometrium. This can interrupt the delicate hormonal environment needed for successful conception and implantation.
Research has shown that women with adenomyosis can have a significantly decreased pregnancy rate, estimated at 26.8%. In comparison, women without the condition have a greater pregnancy rate of 37.1%. This speaks to what adenomyosis does to the uterine environment, causing it to be less receptive to a fertilized egg.
Effects on Pregnancy Outcomes
Fertility pregnancy outcomes in women with adenomyosis may be poorer, with lower cumulative pregnancy rates reported. For patients with only adenomyosis, the cumulative rate is 19%. In comparison, this rate increases to 82% for individuals with solely endometriosis.
Treatment with GnRH-a prior to IVF has remarkable potential. It seems to prepare the endometrium very well and increase clinical pregnancy rates. However, women with adenomyosis continue to struggle to achieve pregnancy even after these interventional measures. Just 23.6% are successful versus 44.6% of adenomyosis-free women getting pregnant.
Links to Infertility Challenges
We often associate adenomyosis with difficulties getting pregnant. As adenomyosis affects reproductive-aged women, over half of these patients are affected by infertility. Of these, 16.50% experience IVF failure rates and 8.74% face recurrent miscarriages.
Women in their late 30s and 40s are most affected by this condition. Women in this age group frequently experience the consequences of delayed childbearing. With the advent of GnRH-a therapy, there are successful treatment avenues available. Because of this strategy, a healthy baby girl was delivered after only 16 weeks of treatment.
Diagnosing Adenomyosis
Medical History and Physical Exam
When diagnosing adenomyosis, a thorough medical history and physical exam set the stage. It starts with identifying clinical symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding or pelvic pain and reviewing a patient’s history of infertility.
On physical exam, a tender, enlarged uterus can be palpated, which can be suggestive of adenomyosis. This first step is crucial to rule out other conditions that have similar symptoms, helping to inform further diagnostic tests.
Imaging Techniques for Diagnosis
Imaging plays a vital role in confirming adenomyosis. Two main techniques stand out: ultrasound and MRI. Features on a 3D transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) often include an irregular junctional zone and significant variations in thickness, with more than 0.3 inches.
The sensitivity of 3D ultrasound remains uncertain. MRI, with a sensitivity of 77% and specificity of 89%, provides a clearer picture, especially in complex cases with other uterine issues like fibroids. MRI findings such as a large uterus and a junctional zone thicker than 0.5 inches are considered diagnostic.
Classification of Adenomyosis
Classification has developed over the years, with systems based on imaging and histological results. These classifications are intended to support understanding of the disease’s extent, which can vary significantly.
Recent studies suggest a prevalence of 7.5% in young, infertile women when diagnosed with 2D-TVUS.
Managing Adenomyosis for Better Fertility
1. Lifestyle Changes and Diet
Getting control over adenomyosis starts with improving your overall fertility health with lifestyle and diet. Eating a healthy diet including plenty of anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids is important.
Exercise is very beneficial to overall health and can help reduce symptoms. Herbal supplements such as ginger and turmeric are known for their anti-inflammatory effects. Maintaining a low stress level via yoga, meditation, and other stress-reducing activities helps.
2. Medications and Hormonal Treatments
Medications play the key role in managing adenomyosis. As with endometriosis, hormonal treatments—including GnRH agonists—are central. Long-term suppression with GnRH-a, for 2 to 4 months prior to IVF, greatly increases pregnancy and implantation rates.
Research indicates reduced progesterone receptor expression in adenomyosis women, calling for more individualized hormonal treatments. Interestingly, two of the cases conceived within 6 months after a short course of GnRH therapy.
3. Surgical Options and Procedures
Surgery provides a second path, especially for women with debilitating symptoms. Conservative surgeries yield good pregnancy rates (25% to 61.5%) but with miscarriage rates as high as 25%.
Fertility-enhancing invasive procedures, such as uterine-sparing surgery, can be clinically beneficial when performed using the treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding.
4. Assisted Reproductive Technologies
For those living with adenomyosis, assisted reproductive technologies cannot be overstated. Techniques such as IVF, particularly following GnRH-a treatment, have demonstrated higher success rates.
Each increase in average JZ over 0.28” raises the risk of implantation failure. This underscores the need for careful monitoring at the time of treatment.
5. Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
Ongoing management is essential. Routine management and follow-up can ensure continuing evaluation of treatment effectiveness and modification of treatment plans when necessary.
Regular follow-up allows for any concerns to be detected early, keeping your fertility in great health.
Treatment Options and Fertility Implications
Non-Surgical Treatments and Their Benefits
When fertility preservation is a goal, non-surgical treatments are frequently used as a first-line option to address adenomyosis. GnRH-a therapy is often preferred because it preps the endometrium, as well as reducing symptoms. Long-term GnRH-a treatment of 2 to 4 months increases clinical pregnancy and implantation rates significantly.
This can be especially beneficial when done in advance of a frozen embryo transfer. Depending on GnRH-a alone could fall short of producing the best outcomes. In one case, after 16 weeks of treatment, a healthy male infant was delivered, demonstrating its potential efficacy.
Additionally, 7.5% of young infertile women are diagnosed with adenomyosis, but the combination approach usually works best.
Surgical Treatments and Fertility Outcomes
Surgical treatments are usually pursued when non-surgical treatments fail to relieve symptoms and/or enhance fertility. Conservative surgery, which consists of radical procedures such as cytoreductive surgery, provides excellent results. Almost 2365 women had such intervention with postoperative pregnancy rates varying from 17.5% to 72.7%.
Importantly, conservative surgery plus GnRH-a had greater cumulative 3-year clinical pregnancy and delivery rates than GnRH-a alone. When performed in younger patients with full adenomyosis removal, 50% have delivery; results decline with age. For women greater than 40 years, pregnancy rates stay low after surgery.
Alternative Therapies and Considerations
With alternative therapies, there are more avenues to explore adenomyosis management and fertility preservation. Though traditional treatments are still the mainstay, some people might turn to changes in diet, acupuncture, or herbal medicine.
These alternatives frequently serve to enhance medical treatments, delivering whole person benefits. Guidance is important, especially when looking to take integrative approaches. Microsurgical cytoreduction in conjunction with GnRH-a provides promising new hope for patients.
This strategy may benefit patients who are non-responders to GnRH-a monotherapy or unable to tolerate extended treatment times.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Coping with Diagnosis and Treatment
Living with adenomyosis poses a variety of issues. Patients are frequently countered with unfamiliarity, which can further complicate the challenge of handling everyday life. These challenges create an emotional burden that manifests as anxiety, depression, and stress.
Over one quarter (28.9%) of patients experience anxiety, with 10% experiencing moderate to severe anxiety. This emotional toll takes a toll on relationships, highlighting the need for emotional and psychological support. Now more than ever, professional health education and psychosocial support are key.
They can support patients by navigating through treatment options, assist in better understanding their condition, and provide coping strategies. Support that is personalized, holistic, and specific to individual needs can help lift the emotional burden and help patients thrive despite the condition.
Support Groups and Counseling Options
Emotional and social support are key components in managing adenomyosis and helping it fit into your life. Patients who are already heavily affected by feelings of isolation and stigma find their emotional and psychological sufferings further deepened.
Support groups offer the opportunity to share with others who are going through what you are, creating a comforting feeling of connection and acceptance. Counseling can help you work through these emotional hurdles, offering you tools to help you cope with anxiety and stress.
These options are extremely important, because without support, symptoms can worsen. Personalized emotional and psychological support is just as important as the physical side when living with adenomyosis. It offers hands-on assistance and psychoemotional support, resulting in improved physical and mental health.
Conclusion
Although managing adenomyosis while trying to conceive can seem overwhelming, options are available. Knowledge of your body and knowledge of the right medical advice goes a long way. Treatments such as hormone therapy or surgery provide avenues to improved fertility. Each step forward toward better adenomyosis treatment takes us that much closer to a wonderfully rewarding outcome. Emotional support from friends, family, or professionals makes for a smoother and more comfortable journey. Just keep in mind, knowledge and advocacy are your best friends, which will light the way down the road ahead. You’re not the only one fighting this battle, and every ounce of energy invested makes a difference. Contact a healthcare professional today, find out what options are available, and reclaim your fertility journey. Look for their directions, be aware, and regain control over your health and fate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis, a condition where the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows into the uterus’ muscular wall, is more prevalent among adenomyosis patients with uterine fibroids. This often results in heavy and painful periods, severe cramping, and debilitating pelvic pain. Typically affecting women in their thirties and forties, proper diagnosis and infertility treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
How does adenomyosis affect fertility?
Adenomyosis impacts female fertility by altering the uterine environment, which thins the endometrium and complicates embryo implantation. This condition can also result in heavy or painful periods. Fortunately, early diagnosis and effective infertility treatment can significantly enhance fertility outcomes for patients attempting to conceive.
How is adenomyosis diagnosed?
Adenomyosis is diagnosed through imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or MRI, along with a complete gynecological exam. To rule out other conditions, your doctor may run additional tests. If you suspect you have adenomyosis, particularly if you’re experiencing fertility problems, talk to your healthcare provider.
Can adenomyosis be managed to improve fertility?
Of course, improving adenomyosis symptoms and fertility outcomes go hand in hand. The main treatment approach for adenomyosis patients includes medication to alleviate symptoms, along with uterine surgery as needed. Lifestyle changes, including sticking to a healthy diet and getting regular exercise, can also help reduce symptoms. Speak with your healthcare provider to create a plan that’s right for you.
What are treatment options for adenomyosis and their fertility implications?
Treatment options for adenomyosis include pain relievers, hormone therapy, and surgical interventions like endometrial ablation. However, certain treatments can affect fertility outcomes, such as hysterectomy, which removes the womb entirely and eliminates any chance of pregnancy. Discuss with your doctor the risks and benefits to support your fertility goals.
How can emotional and psychological support help?
Emotional and psychological support is integral to managing adenomyosis patients. Becoming active in support groups and/or seeking counseling can help reduce stress and promote mental well-being, which may improve fertility outcomes and assist them in better coping with the condition.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage adenomyosis?
Yes, lifestyle changes can help manage adenomyosis, a gynecological disorder that affects female fertility. A healthy diet with regular exercise, along with getting enough sleep, goes a long way. Stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation are beneficial as well, significantly enhancing the fertility outcome for adenomyosis patients.
