Posted November 06, 2024 in Uncategorized
17 minute read
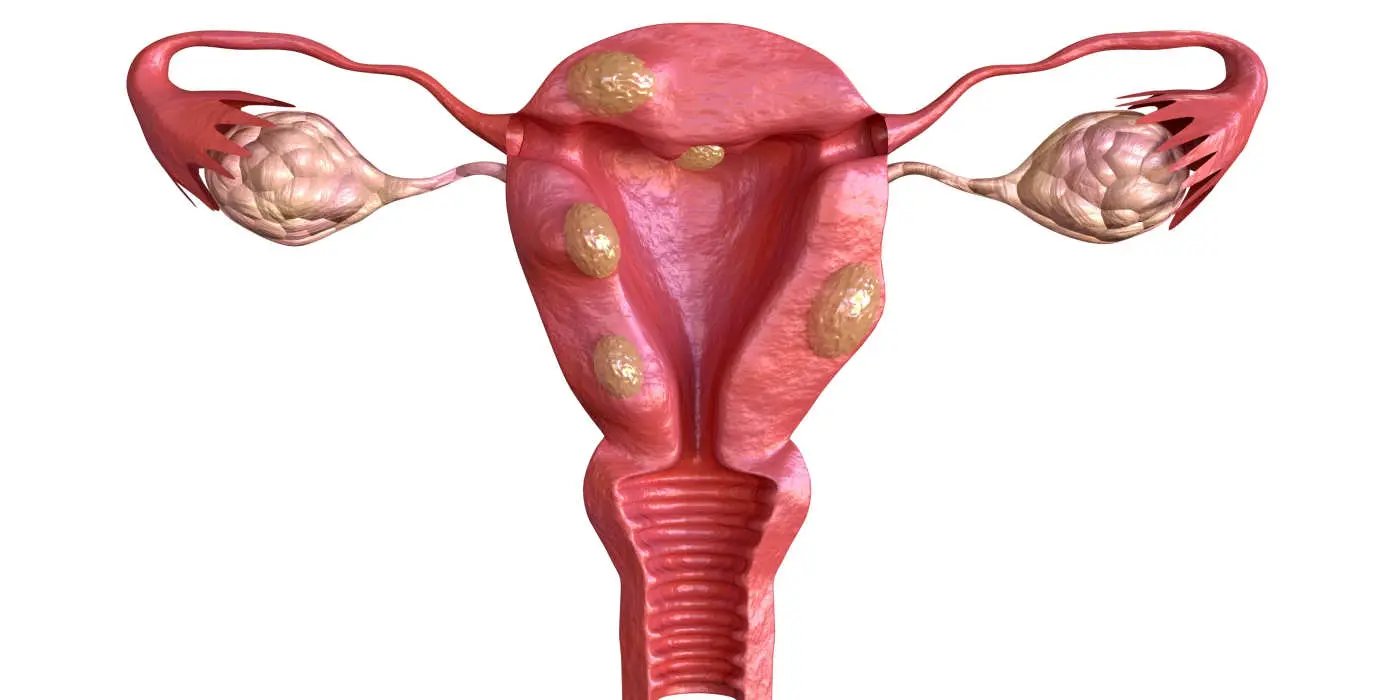
Did you know that up to 80% of women develop fibroids by age 50? These non-cancerous growths can affect fertility, making it tough for many women to conceive. Fertility treatments for women with fibroids offer hope and solutions tailored to individual needs, using symptom management.
Understanding the right options is crucial. Treatments for uterine fibroids can range from medication to surgical interventions, each with its own benefits for many fibroids. Women need to know how fibroids impact their reproductive health and what steps they can take. This post will explore effective fertility treatments available for women facing this challenge. Get ready to discover valuable insights and empower your journey toward motherhood.
Key Takeaways
- Understand how fibroids can impact your fertility by learning about their size and location. This knowledge can help you discuss concerns with your healthcare provider.
- If you have fibroids, consider consulting a fertility specialist who can evaluate your situation and recommend the best management strategies tailored to your needs.
- Explore various treatment options like medication or surgery, which may help improve your chances of conception. Discuss these options with your doctor to find what works best for you.
- Be aware of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) that can aid in conception if fibroids are present. Techniques like IVF might be beneficial depending on your specific case.
- Research differences between uterine artery embolization and myomectomy to understand which surgical option may be more suitable for your fertility goals.
- Stay informed about pregnancy success rates after fibroid treatment, as many women go on to have healthy pregnancies following appropriate management.
Understanding Fibroids and Fertility
Definition and Prevalence
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They are also known as fibroid tumors or fibroid disease. About 70% to 80% of women will have fibroids by age 50. Many women may not even know they have them. This is because fibroids often do not cause noticeable symptoms. However, for some, uterine fibroid complications can lead to issues with fertility.
Impact on Reproductive Functions
Fibroids can disrupt normal reproductive functions in several ways. Their size and location matter greatly. Subserosal fibroids, which grow on the outer wall of the uterus, can distort the shape of the uterus. This distortion can interfere with implantation, affecting uterine receptivity.
Larger fibroids can also block the fallopian tubes. This blockage, possibly due to a uterine fibroid, prevents sperm from reaching the egg or the fertilized egg from traveling to the uterus. Fibroids may change the blood flow to the endometrium, impacting its development and function. If the endometrial cavity is altered, it may not support a pregnancy well.
Complications Related to Fibroids
Women with fibroids might experience various complications that affect their ability to conceive. These include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain
- Miscarriage risk
The presence of fibroids can lead to challenges during pregnancy as well, such as premature birth or placental abruption.
Recognizing Fibroids in Evaluations
Recognizing fibroids is crucial during infertility evaluations. Health care providers often conduct imaging tests like ultrasounds or MRIs to identify uterine fibroids. Ignoring fibroids can delay treatment and worsen fertility issues.
Understanding different fibroid types is important too. For example, subserous fibroids may pose less of a problem than those located within the uterine cavity, called submucosal fibroids. The latter can significantly impact fertility due to their direct interference with the endometrial lining and uterine fibroid.
Fibroid Size and Growth Rates
The size of fibroids plays a role in how they affect fertility. Smaller fibroids might not cause any issues, while larger ones could be more problematic. Studies show that as fibroid volume increases, so do potential complications.
Monitoring fibroid growth rates is essential for women trying to conceive. Regular check-ups help assess if treatment is necessary based on changes in size or symptoms.
How Fibroids Affect Conception
Mechanisms of Obstruction
Fibroids can significantly impact conception. They may obstruct the fallopian tubes. This obstruction prevents the sperm from reaching the egg. It also hinders the transport of the fertilized egg to the uterus. The presence of fibroids can cause inflammation and scarring in the pelvic area. This creates a barrier that affects gamete transport.
Endometrial Alterations
Fibroids also alter the endometrial cavity. This change can affect embryo implantation. An altered cavity may not provide a suitable environment for an embryo to attach. Submucosal fibroids are particularly concerning in this regard. They grow within the uterine lining and can disrupt normal implantation processes. This disruption can lead to failed pregnancies or miscarriages.
Types of Fibroids and Their Impact
Understanding the types of fibroids is crucial. There are three main types: submucosal, intramural, and subserosal. Each type affects conception differently.
- Submucosal fibroids grow just beneath the uterine lining. They are linked to more significant fertility issues due to their direct impact on the endometrium.
- Intramural fibroids develop within the uterine wall. These can distort the shape of the uterus, which may interfere with implantation as well.
- Subserosal fibroids grow on the outer wall of the uterus and generally have less direct impact on conception compared to other types.
The location and size of these fibroids matter greatly when considering fertility treatments.
Importance of Diagnosis
Proper diagnosis is essential for women with fibroids who wish to conceive. Healthcare providers often use ultrasound or MRI to identify fibroid types and sizes. Knowing this information helps in planning effective treatment options.
Women should discuss their specific situation with a healthcare provider. Understanding how each type of fibroid affects conception allows for better management strategies.
Emotional Considerations
Dealing with fertility issues can be emotionally challenging. Women may experience anxiety and stress related to conceiving with fibroids. Support from family, friends, or counseling services can help navigate these feelings.
Managing Fibroids for Better Fertility
Regular Monitoring
Women planning to conceive should regularly monitor their uterine fibroids. This is crucial, especially if they have multiple fibroids or large fibroids. Regular check-ups can help track the size and growth of these growths. Studies show that some women may experience fibroid regression, where fibroids shrink over time. Monitoring helps identify any changes that could impact fertility.
Healthcare providers often recommend ultrasound examinations. These tests provide clear images of the uterus. They help assess the condition of intramural fibroids and other types. This information allows doctors to suggest appropriate treatment options.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can also help manage symptoms associated with fibroids. Women might consider incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Research indicates that maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of developing new fibroids.
Regular exercise is another effective strategy. Physical activity can alleviate some symptoms like pain and bleeding. It also promotes overall well-being, which is essential for women trying to conceive.
Avoiding processed foods and excessive sugar may also be beneficial. Some studies suggest that high sugar intake can worsen symptoms related to fibroid risk.
Dietary Adjustments
Dietary adjustments play a significant role in managing fibroid symptoms. Foods high in fiber can aid digestion and help maintain hormonal balance. This balance is important for ovarian function and overall reproductive health.
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods may also help reduce pain associated with fibroids. Foods like fatty fish, nuts, and leafy greens contain properties that fight inflammation.
Certain supplements may support fibroid management as well. For example, vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids are known for their positive effects on reproductive health. Consulting a healthcare provider before starting any supplement is advisable.
Healthcare Consultation
Consulting healthcare providers is vital for personalized management strategies. Each woman’s situation with fibroids can differ significantly. A healthcare professional can provide tailored advice based on specific needs.
e women may need medications such as progestins to manage heavy bleeding or pain caused by fibroids. Others might require surgical interventions if they have huge or symptomatic fibroids affecting fertility.
Discussing all available options helps women make informed decisions about their health.
Fibroids and Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Impact on Success Rates
Fibroids can significantly reduce the success rates of assisted reproductive technologies (ART). These uterine masses may interfere with implantation. They can distort the shape of the uterus, affecting how an embryo attaches. Studies show that fibroids can lead to lower pregnancy rates in infertile women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF).
The presence of fibroids can also increase the chances of complications. For instance, women with fibroids have higher risks of spontaneous abortion. This means that even if implantation occurs, the pregnancy may not continue. The abnormal endometrium caused by fibroids can further hinder successful outcomes.
Types of Fibroids
Different types of fibroids affect ART outcomes in various ways. Submucosal fibroids are located just beneath the endometrial lining. They pose the highest risk for complications during ART procedures. These fibroids can directly impact endometrial receptivity, making it difficult for embryos to implant.
Intramural fibroids, which grow within the uterine wall, can also be problematic. They may not affect the cavity directly but can still alter blood flow. This change can influence how well an embryo develops after implantation.
Subserosal fibroids are less likely to impact ART success rates. However, they can still cause issues if they grow large enough to distort the uterus.
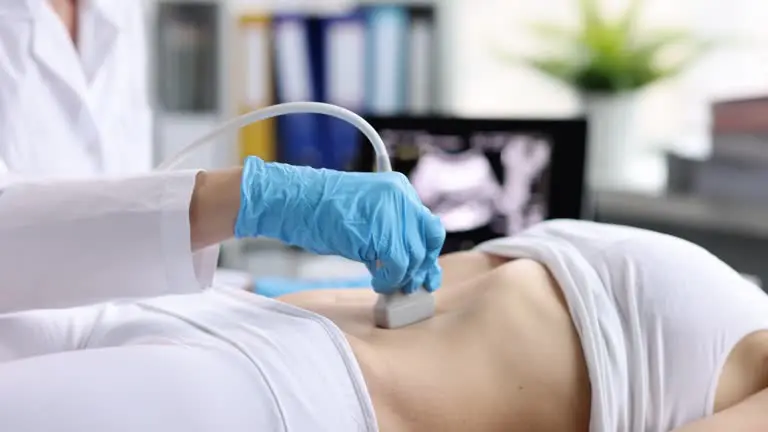
Importance of Pre-ART Assessments
Pre-ART assessments are crucial for evaluating fibroid presence and size. Women considering ART should undergo a thorough examination, including ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These tests help identify and measure fibroid tissue accurately.
Identifying fibroids before starting treatment allows for better planning. If necessary, treatments like fibroid embolization or focused ultrasound can be performed first. This approach helps improve the chances of a successful ART outcome.
Ignoring the presence of fibroids can lead to wasted time and resources. Infertile patients may face additional stress if they undergo procedures without proper evaluation. Knowing about existing fibroids enables doctors to tailor treatment plans effectively.
Medical Treatments for Fibroid Management
Hormonal Treatments
Hormonal treatments are common fibroid treatment options. These therapies aim to regulate hormone levels, which can help reduce fibroid size and symptoms. Medications like birth control pills and hormonal IUDs can manage heavy menstrual bleeding caused by symptomatic fibroids.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists are another effective option. They decrease estrogen and progesterone levels, shrinking uterine fibroids. However, these treatments are temporary and can lead to side effects such as hot flashes and bone density loss.
Non-Hormonal Therapies
Non-hormonal therapies also exist for managing fibroids. These include medications like NSAIDs, which help relieve pain and discomfort. Pain management is crucial for those suffering from fibroid-related symptoms.
e doctors recommend tranexamic acid to reduce heavy bleeding. This medication works by stabilizing blood clots, making it easier to manage heavy periods without surgery.
Surgical Options
Surgical procedures may be necessary for severe cases of fibroids. Myomectomy is a common surgery that removes fibroids while preserving the uterus. This option is suitable for women who wish to maintain fertility.
In cases where fibroids cause significant issues, a hysterectomy might be recommended. This procedure involves removing the entire uterus and is considered a permanent solution.
Uterine Artery Embolization
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) is another innovative treatment for uterine fibromyomas. This minimally invasive procedure blocks blood flow to fibroids, causing them to shrink over time. UAE is effective for reducing symptoms and does not require a long recovery period.
Effectiveness of Treatments
The effectiveness of these fibroid treatments varies by individual case. Some women find relief with hormonal therapies, while others may need surgical intervention. It’s essential to discuss all available options with a healthcare provider.
Choosing the right treatment depends on factors like the size and location of fibroids, symptoms, and personal health goals. Each woman’s situation is unique, so tailored approaches work best.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain management plays a critical role in the overall treatment plan for women with symptomatic fibroids. Over-the-counter medications can help alleviate discomfort associated with menstrual cramps or pelvic pressure.
In some cases, physical therapy or acupuncture may provide additional relief. These complementary therapies can enhance well-being and improve quality of life.
Surgical Options for Fibroid Removal
Types of Surgery
Fibroid removal can occur through various surgical techniques. Myomectomy is a common option. This procedure removes fibroids while preserving the uterus. It can be done through different methods, such as hysteroscopy, laparoscopy, and laparotomy.
Hysteroscopy involves inserting a thin tube through the vagina and cervix to remove fibroids located inside the uterus. This method is less invasive and has a quicker recovery time. Laparoscopy uses small incisions in the abdomen to access and remove fibroids. This technique also minimizes scarring.
Laparotomy is more invasive. Surgeons make a larger incision in the abdomen for direct access to the uterus. This method is often used for larger or multiple fibroids. Each technique has its advantages based on the size and location of the fibroids.
Criteria for Surgery
Choosing the right surgical option depends on several factors. The size and location of the fibroids play crucial roles. Subserosal fibroids are located on the outer wall of the uterus, while submucosal ones grow inside the uterine cavity. The former may not affect fertility as much as submucosal fibroids.
Patient health is another important factor. Surgeons consider overall health, age, and future pregnancy plans before recommending surgery. Women with larger fibroids or severe symptoms may need surgical intervention sooner.
Benefits for Fertility
Surgical intervention can significantly improve fertility outcomes for women with fibroids. Removing fibroids can relieve symptoms like heavy bleeding and pain. These conditions can interfere with conception.
Studies show that women who undergo myomectomy have higher pregnancy rates compared to those who do not receive treatment. By removing obstructive fibroids, surgeons help create a more favorable environment for implantation.
e procedures, like hysteroscopy, allow for quicker recovery times. Women can return to normal activities sooner, including attempts to conceive.
In summary, surgical options provide effective solutions for women dealing with fibroids. Myomectomy remains a primary choice among various techniques. Factors such as size, location, and patient health guide decisions about surgery. Fertility outcomes often improve after surgical interventions, making these options valuable for many women.
Comparing Uterine Artery Embolization and Myomectomy
Goals of Treatment
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) aims to reduce blood flow to fibroids. This can lead to their shrinkage. Patients often seek UAE for symptom relief without major surgery.
Myomectomy focuses on removing uterine fibroids while preserving the uterus. The goal is to eliminate symptoms and maintain fertility. Doctors perform various types of myomectomies, including hysteroscopic, laparoscopic, and abdominal approaches. Each method has specific indications based on the size and location of the fibroids.
Recovery Times
Recovery times differ significantly between UAE and myomectomy. After UAE, most women return to normal activities within a week. Some may experience mild discomfort or cramping.
Myomectomy requires a longer recovery period. Hysteroscopic myomectomy usually allows for a quicker recovery of about two weeks. Laparoscopic myomectomy involves small incisions, leading to a recovery time of three to four weeks. Abdominal myomectomy typically has the longest recovery, lasting six to eight weeks due to larger incisions.
Potential Complications
Complications can arise from both procedures. UAE may lead to complications such as uterine perforation or infection. Rarely, it can cause uterine rupture in future pregnancies.
Myomectomy carries its own risks, including bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding organs. Specific risks like partum hemorrhage may occur during delivery if significant scarring develops from the procedure.
Long-term Effects on Fertility
Both treatments affect fertility differently. UAE may impact uterine contractility and overall uterine volume. Studies suggest that while many women conceive after UAE, there might be a higher risk of complications during pregnancy.
Myomectomy generally offers better outcomes for women seeking to become pregnant. It preserves the uterus and can improve fertility rates. However, fibroid recurrence is possible, which could require further treatment.
Recurrence Rates
Fibroid recurrence is a concern with both procedures. Research shows that about 10-30% of women experience new fibroid growth after UAE within five years. These new growths may not always require additional treatment.
Recurrence rates for myomectomy depend on the technique used and individual factors. Women undergoing laparoscopic or hysteroscopic myomectomies have lower recurrence rates compared to abdominal myomectomies.
Pregnancy Success After Treatment
Pregnancy Rates
Pregnancy rates can vary after treatment for fibroids. Research shows that women who undergo myomectomy have pregnancy rates ranging from 60% to 80%. Uterine artery embolization (UAE) also shows promising results, with pregnancy rates of about 55% to 70%. These statistics highlight the potential for successful pregnancies following treatment.
Influencing Factors
Several factors affect the success of pregnancies after fibroid treatment. Age plays a significant role. Women under 35 generally have higher pregnancy rates compared to older women. The size and location of fibroids also matter. Larger fibroids or those located in the uterine cavity may lead to complications. Understanding these factors helps women set realistic expectations.
Follow-Up Care
Follow-up care is essential after fibroid treatment. Regular monitoring can help detect any complications early. Women should have their first prenatal visit scheduled as soon as they confirm their pregnancy. This allows healthcare providers to assess the uterus and check for any issues related to fibroids.
Monitoring during pregnancy can lead to better obstetrical outcomes. Healthcare providers may recommend additional ultrasounds to observe the growth of the placenta and monitor for preterm labor signs. Keeping an open line of communication with doctors is vital.
Miscarriage Rates
Miscarriage rates can be a concern for women with a history of fibroids. Studies indicate that the miscarriage rate after treatment is similar to that of the general population, around 10% to 15%. However, some women may still face challenges due to underlying health issues or other risk factors.
Clinical Outcomes
Clinical outcomes improve significantly after proper treatment for fibroids. Women who have undergone myomectomy often report fewer complications during pregnancies. They experience lower rates of preterm delivery and higher live birth rates compared to those who do not receive treatment.
Recovery times also play a role in pregnancy success. Most women recover from myomectomy within six to eight weeks, while UAE recovery may take less time. Shorter recovery times allow women to plan their pregnancies sooner.
Importance of Progesterone
Progesterone is crucial for maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Women who have had fibroid treatments may need progesterone supplements if levels are low. This hormone supports the placenta and reduces the risk of miscarriage.
Closing Thoughts
Navigating fertility treatments with fibroids can feel daunting, but understanding your options empowers you. From managing fibroids to exploring assisted reproductive technologies, you have the tools to enhance your chances of conception. Each treatment path offers unique benefits tailored to your needs.
Take charge of your journey. Consult with healthcare professionals who specialize in fibroid management and fertility. Together, you can devise a plan that suits your situation. Your dreams of starting or expanding your family are within reach. Don’t wait—explore your options today and make informed decisions for a brighter future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are fibroids?
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in the uterus. They can vary in size and number, often affecting women’s reproductive health.
How do fibroids impact fertility?
Fibroids can block the fallopian tubes, alter the uterine lining, or affect blood flow, making conception more challenging.
Can women with fibroids get pregnant?
Yes, many women with fibroids can conceive. However, treatment may be necessary to improve chances of successful pregnancy.
What treatments are available for fibroids?
Treatment options include medication, surgery (like myomectomy), and minimally invasive procedures such as uterine artery embolization.
Is surgery always required for fibroids?
Not always. Many women manage symptoms with medication or monitoring. Surgery is typically recommended if fibroids significantly affect fertility or cause severe symptoms.
How effective is assisted reproductive technology (ART) for women with fibroids?
ART can be effective for women with fibroids. Success rates depend on individual circumstances, including fibroid size and location.
What are the chances of a successful pregnancy after treating fibroids?
Success rates vary. Generally, many women experience improved fertility and higher success rates after appropriate treatment for fibroids.
