Posted December 02, 2024 in Fertility Blog & Information
16 minute read
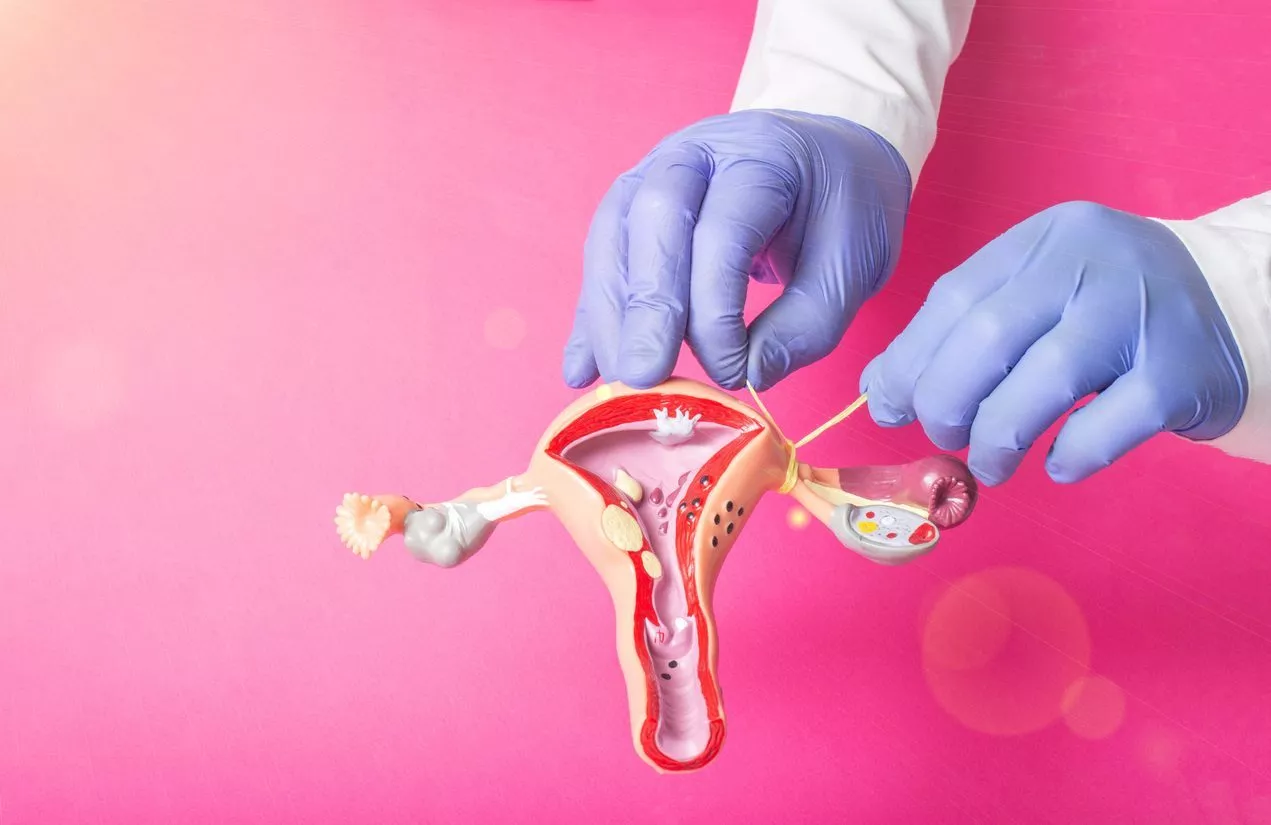
Have you considered your fertility options after tubal ligation? Many people face uncertainty after this procedure. It’s crucial to know that there are pathways, such as a gestational surrogate or pregnancies ivf, to expand your family with a male partner if needed, even if a fallopian tube is not available. From reversal surgery to assisted reproductive technologies, options exist for those wanting to conceive.
Understanding these choices can empower you in making informed decisions. Each option has its benefits and challenges, but with the right information, you can navigate this journey confidently in the tube. Explore the possibilities and take control of your reproductive health. Your dreams of parenthood may still be within reach.
Key Takeaways
- Tubal ligation is a permanent form of birth control, but pregnancy may still be possible through various options.
- For those wishing to conceive after tubal ligation, consider tubal reversal surgery or in vitro fertilization (IVF) as viable paths.
- Tubal reversal surgery can restore fertility but may not be suitable for everyone; consult with a specialist to assess your individual case.
- IVF offers an alternative for women who may not be candidates for surgery, allowing for pregnancy without needing to reverse the ligation.
- Female age plays a significant role in fertility; younger women generally have better success rates with both tubal reversal and IVF.
- Financial planning is crucial, as both treatments can be costly; research insurance coverage and explore financing options to manage expenses.
Understanding Tubal Ligation
Definition
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure. It serves as a permanent form of birth control for women. During this operation, the fallopian tubes are blocked or sealed. This prevents eggs from traveling from the ovaries to the uterus. As a result, fertilization cannot occur.
Procedure
The procedure for tubal ligation varies. Surgeons may use different methods to perform the surgery. The most common techniques include:
- Laparoscopy: This minimally invasive method involves small incisions in the abdomen. A camera and instruments are inserted to block the tubes.
- Mini-laparotomy: This involves a larger incision but is often performed shortly after childbirth.
- Hysteroscopic sterilization: This technique uses a scope inserted through the vagina to place devices in the tubes.
Each method has its own risks and benefits. Recovery time also varies depending on the technique used.
Reasons for Choosing Tubal Ligation
Women choose tubal ligation for various reasons. Many consider it when they feel their family is complete. Others may have health concerns that make pregnancy risky.
e common reasons include:
- Family planning: Women who have children may decide they do not want more.
- Health issues: Certain medical conditions can complicate pregnancy.
- Age considerations: Older women may feel they have passed their childbearing years.
These decisions are often made after careful consideration and consultation with healthcare providers.
Emotional Impact
Choosing tubal ligation can be emotional. Some women feel relief knowing they won’t face unplanned pregnancies. Others may experience regret later on. It’s important for women to discuss feelings and options before the surgery.
Risks and Considerations
Like any surgery, tubal ligation carries risks. Possible complications include infection or injury to surrounding organs. Some women may experience changes in menstrual cycles post-surgery.
Understanding these factors is crucial before deciding on this method of birth control.

Pregnancy After Tubal Ligation
Possibility of Pregnancy
Pregnancy can still happen after tubal ligation. This procedure is meant to prevent pregnancies by blocking the fallopian tubes. However, the pregnancy rate post-ligation is about 1 in 100 women each year. Some women may experience unexpected pregnancies even years later.
Factors such as age and health can influence these rates. Women who undergo tubal sterilization at a younger age may have higher chances of pregnancy later on. This possibility can be surprising for many.
Ectopic Pregnancies
Ectopic pregnancies are a serious concern after tubal ligation. These occur when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in a fallopian tube. The tubal pregnancy rate is higher among women with a history of tubal ligation.
This condition requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms include sharp pain and abnormal bleeding. Ectopic pregnancies can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly.
Emotional Impacts
Unexpected pregnancies after tubal ligation can bring various emotional responses. Many women feel shock or confusion upon learning they are pregnant again. This situation can lead to feelings of anxiety and stress.
Women may also face societal pressures regarding their decisions about family planning. They might feel guilt or disappointment if they were sure they didn’t want more children. Support from family and friends becomes crucial during this time.
Psychological Effects
The psychological effects of an unexpected pregnancy can be profound. Women may struggle with their identity as a parent or their future plans. They might question their choices and feel overwhelmed by the new circumstances.
Counseling can help women process these feelings. Speaking with a professional allows them to explore their emotions in a safe space. Sharing experiences with others who faced similar situations can also provide comfort.
Tubal Reversal Surgery Overview
Surgical Process
Tubal reversal surgery aims to restore fertility after a tubal ligation. This procedure reconnects the fallopian tubes, allowing eggs to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. Surgeons perform this operation using two main techniques: laparoscopic and open surgery.
Laparoscopic tubal reversal is less invasive. It uses small incisions and a camera for guidance. This method typically results in quicker recovery times compared to open surgery. The surgeon removes scar tissue and reanastomoses the tubes. Open surgery involves a larger incision and provides more direct access but may lead to longer recovery.
The success of tubal reversal depends on various factors. These include the type of ligation performed, the woman’s age, and overall health. Successful reversal can lead to natural conception in many women.
Risks and Complications
Like all surgeries, tubal reversal carries risks. Potential complications can include infection, bleeding, or damage to surrounding organs. Some women may experience ectopic pregnancy after the procedure. This occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, which can be life-threatening.
Other risks involve anesthesia reactions and scarring within the abdomen. Women should discuss these risks with their healthcare provider before proceeding. Understanding these potential complications is crucial for making an informed decision.
Consulting a Specialist
Consulting with a fertility specialist is essential before undergoing tubal ligation reversal surgery. Specialists assess individual circumstances and provide tailored advice. They may recommend tests to evaluate reproductive health and determine if surgery is appropriate.
A fertility expert can also outline alternative options for those who may not be candidates for surgery. These alternatives might include in vitro fertilization (IVF) or other assisted reproductive technologies.
Informed decisions lead to better outcomes. A thorough understanding of the surgical process, potential risks, and available options plays a vital role in family planning after tubal ligation.
In Vitro Fertilization Explained
IVF Process
IVF, or in vitro fertilization, is a method to help women conceive. The process starts with ovulation stimulation. Doctors prescribe fertility medications to encourage the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. This increases the chances of successful fertilization.
After stimulation, doctors perform egg retrieval. They use a thin needle, guided by ultrasound, to collect eggs from the ovaries. This procedure usually requires sedation for comfort. Once the eggs are retrieved, they are placed in a lab dish with sperm. This allows for fertilization to occur.
Once fertilized, the embryos develop for several days. Doctors monitor their growth closely. After this period, one or more healthy embryos are selected for transfer into the uterus. This step is known as embryo transfer. A thin catheter guides the embryo through the cervix and into the uterus.
Fertility Medications
Fertility medications play a crucial role in IVF cycles. These drugs help stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs rather than just one. Common medications include gonadotropins and Clomiphene citrate.
These medications can cause side effects such as mood swings or bloating. However, they significantly increase the chances of successful pregnancies through IVF.
Bypassing Fallopian Tubes
IVF is particularly beneficial for women who have undergone tubal ligation. This procedure blocks or seals the fallopian tubes. As a result, natural conception becomes impossible. IVF bypasses these tubes entirely.
During IVF, fertilization occurs outside of the body. Sperm and egg meet in a laboratory setting rather than in the fallopian tubes. This method eliminates concerns about blocked tubes or ectopic pregnancies that can occur when fertilization happens in the wrong place.
Women with a history of ectopic pregnancies may find IVF especially appealing. Since IVF does not rely on the fallopian tubes, it reduces risks associated with these complications.
Costs of IVF
The cost of IVF can vary widely based on location and clinic services. On average, a single cycle of IVF may cost between $12,000 and $15,000 in the United States. Additional expenses may include medications and embryo freezing.
Insurance coverage for IVF varies by state and individual plans. Some insurance companies cover part of the costs while others do not. It’s essential to check your policy details before starting treatment.
Comparing Tubal Reversal and IVF
Recovery Time
Tubal reversal requires surgery. This procedure connects the fallopian tubes again. Recovery typically takes about four to six weeks. Women may experience pain and discomfort during this period.
In contrast, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is less invasive. The process involves hormone injections, egg retrieval, and embryo transfer. Recovery from IVF is usually shorter, often just a few days. Many women return to normal activities quickly after the procedure.
Success Rates
Success rates vary significantly between tubal reversal and IVF. For women under 35, tubal reversal has a success rate of about 70-80%. However, this rate decreases as age increases. For women aged 35-40, it drops to around 50-60%.
IVF offers different success rates based on age as well. For those under 35, the success rate can reach up to 50% per cycle. Women aged 35-40 see this rate decline to about 30-40%. Over 40, the success rate for both methods diminishes further.
Long-term Implications
Long-term implications differ for each option. Tubal reversal can restore natural fertility. However, it does not guarantee future pregnancies. There is also a risk of ectopic pregnancy, which can be dangerous.
IVF provides more control over the timing of pregnancy. It allows for genetic testing of embryos before implantation. This can reduce the risk of inherited conditions. Yet, IVF may require multiple cycles to achieve pregnancy. Costs can accumulate quickly with each attempt.
Price Considerations
The price of tubal reversal varies widely. It can range from $5,000 to $15,000 depending on the surgeon and location. Insurance coverage may not always apply.
IVF costs are generally higher, averaging between $12,000 to $15,000 per cycle. Additional expenses include medications and potential storage fees for embryos. Insurance coverage for IVF also varies by plan and state.
Assessing Tubal Status
Evaluating the tubal status is crucial for women considering fertility options after tubal ligation. The condition of the fallopian tubes can significantly impact the success of treatments like tubal reversal or in vitro fertilization (IVF). Understanding how these tubes function helps in making informed decisions.
Diagnostic Tests
Several diagnostic tests can assess tubal patency and health. A hysterosalpingogram (HSG) is a common procedure. It involves injecting dye into the uterus and fallopian tubes. X-rays capture images to reveal any blockages or abnormalities. This test shows whether the tubes are open and functioning properly.
Another option is a sonohysterogram, which uses saline instead of dye. This test evaluates the uterine cavity and checks for issues that could affect fertility.
Laparoscopy can also be performed. During this minimally invasive surgery, doctors can directly observe the fallopian tubes’ condition. They can identify any scarring or damage that may exist.
Tubal Length and Condition
The length and condition of the fallopian tubes play a vital role in determining the success of reversal surgery. Short tubes, often referred to as “short stumps,” may limit the chances of natural conception. If the remaining tube is too short, it may not effectively transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
The condition of the fimbria, which are finger-like projections at the end of each tube, is equally important. Healthy fimbria help capture released eggs during ovulation. Damaged fimbria can hinder this process, leading to lower pregnancy rates.
Women with healthy, longer tubes generally have better outcomes after tubal reversal surgery. Studies show that successful reversals occur more frequently when both tubes are intact and functioning well.
In contrast, women who opt for IVF might not need to worry about tubal condition as much. IVF bypasses the fallopian tubes entirely by implanting embryos directly into the uterus. However, successful IVF still depends on other factors like ovarian reserve and egg quality.
Impact on Treatment Choices
Understanding tubal anatomy guides women in choosing between tubal reversal and IVF. Women with favorable tubal status may benefit more from reversal surgery, while those with significant damage might find IVF more suitable.
Consulting with a fertility specialist helps clarify options based on individual circumstances. Each woman’s situation is unique, so personalized guidance is essential for making informed choices.
Impact of Female Age on Fertility
Egg Quality
Female age significantly affects egg quality and quantity. As women age, their ovaries produce fewer eggs. The decline in egg quality can lead to difficulties in achieving pregnancy. By age 30, a woman’s fertility begins to decrease. By age 35, this decline becomes more pronounced. At 40, the chances of conceiving naturally drop sharply.
Older eggs also have higher rates of chromosomal abnormalities. This increases the risk of miscarriage and genetic disorders. For instance, women over 35 face a higher chance of having babies with Down syndrome. Thus, age plays a crucial role in determining fertility options.
Pregnancy Success Rates
Statistical data shows that success rates for pregnancy vary with age. For tubal reversal, women under 35 have about a 70% chance of pregnancy within two years. However, this rate drops to around 50% for women aged 35-39. Women over 40 see success rates fall below 20%.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) presents another option. For women under 35, the success rate is about 50% per cycle. This rate declines to around 30% for those aged 35-37 and further drops to approximately 15% for women over 40. These statistics illustrate the impact of female age on fertility options.
Timely Decisions
Timely decision-making is important regarding fertility treatments as women age. Delaying treatment can reduce the chances of success. Women should consider their family goals early on. Discussions with healthcare providers can help clarify available options.
Factors such as personal health and lifestyle also play roles in fertility. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding smoking can improve overall reproductive health.
Women facing tubal ligation may need to explore options sooner rather than later. The longer they wait, the more difficult it may become to conceive.
Emotional Considerations
The emotional aspect of fertility cannot be overlooked. Many women feel pressure as they approach their late thirties and forties. Concerns about time and biological clocks often arise during discussions about starting families.
Support from family and friends can ease these worries. Joining support groups or seeking counseling may provide additional help in navigating these feelings.
Financial Considerations for Treatments
Costs Breakdown
Tubal reversal surgery and IVF have different costs. Tubal ligation reversal can range from $5,000 to $15,000. This price often includes the surgeon’s fee, anesthesia, and hospital charges. Additional fees may arise from pre-operative tests and follow-up visits.
IVF costs are typically higher. A single cycle can cost between $12,000 and $15,000. This amount usually covers medications, egg retrieval, fertilization, and embryo transfer. Hidden fees may include laboratory charges and cryopreservation of embryos.
Both options may require multiple attempts to achieve pregnancy. Each additional cycle increases the overall financial burden.
Insurance Coverage
Insurance coverage varies widely. Some plans cover tubal reversal surgery but not IVF. Others might cover IVF partially or not at all. It’s crucial to check with your insurance provider.
Many fertility clinics offer financial assistance programs. These programs help manage costs for patients without insurance coverage. Some clinics provide payment plans or financing options to ease the financial strain.
Long-Term Financial Implications
Choosing between tubal reversal and IVF has long-term financial implications. Tubal reversal may lead to natural conception over time. However, it does not guarantee pregnancy success. The success rate ranges from 40% to 80%, depending on various factors like age and health.
IVF offers a different path with higher upfront costs but potentially quicker results. Success rates for IVF vary from 20% to 50% per cycle based on factors such as age and diagnosis.
Patients should consider their partner’s support in these decisions. Discussing the emotional and financial aspects is vital before proceeding with either option.
Factors Influencing Costs
Several factors affect the overall costs of both treatments:
- Age: Older women may face higher chances of complications.
- Health status: Pre-existing conditions can increase treatment costs.
- Location: Prices differ by region due to local healthcare costs.
Understanding these factors helps patients make informed choices about their fertility options.
Risks and Side Effects
Both procedures carry risks and potential side effects. Tubal reversal may involve surgical risks like infection or damage to surrounding organs. Recovery time typically lasts one to two weeks.
IVF can lead to complications such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) or multiple pregnancies. Patients must weigh these risks against their desired outcomes.
Closing Thoughts
Navigating fertility options after tubal ligation can feel overwhelming. You’ve learned about the available choices, including tubal reversal and IVF. Each option has its pros and cons, influenced by factors like age and finances. Understanding these aspects empowers you to make informed decisions.
Your journey toward expanding your family is unique. Take the time to weigh your options carefully. Consult with fertility specialists who can provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs. Remember, knowledge is power. Explore your possibilities and take the next step toward realizing your dreams of parenthood.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is tubal ligation?
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure that permanently prevents pregnancy by blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes. It is often chosen by women who are certain they do not want more children.
Can I get pregnant after tubal ligation?
Pregnancy after tubal ligation is rare but possible. Some women may experience a natural reversal of the procedure, while others might seek medical interventions like tubal reversal or IVF.
What is tubal reversal surgery?
Tubal reversal surgery reconnects the fallopian tubes to restore fertility. This option is suitable for women who wish to conceive naturally after having undergone tubal ligation.
How does in vitro fertilization (IVF) work?
IVF involves retrieving eggs from the ovaries and fertilizing them with sperm in a lab. The resulting embryos are then implanted into the uterus, bypassing the fallopian tubes entirely.
Which is better: tubal reversal or IVF?
The choice between tubal reversal and IVF depends on individual circumstances. Tubal reversal may allow natural conception, while IVF can be a quicker solution for those with damaged tubes or other fertility issues.
How does age affect fertility after tubal ligation?
Female age significantly impacts fertility. Women over 35 may face decreased egg quality and quantity, making it important to consider options like IVF sooner rather than later.
What are the costs associated with these fertility treatments?
Costs vary widely based on location and specific procedures. Tubal reversal can range from $5,000 to $15,000, while a single IVF cycle typically costs between $12,000 and $15,000, excluding medication and additional services.
