Posted October 05, 2024 in Fertility Blog & Information
18 minute read
Did you know that nearly 1 in 8 couples face challenges, such as a fertility issue, when trying to conceive, often leading them to consider fertility drugs, a predictive fertility test, or a fertility awareness check? Fertility hormone testing explained through hormonal studies can shed light on these issues related to certain hormones and important hormones in hormonal evaluation studies. Understanding your hormones through hormonal studies is crucial for anyone on the journey to parenthood, especially with fertility drugs, male fertility testing, and a fertility awareness check. This testing helps identify imbalances that may affect fertility. It provides insights into ovulation, menstrual cycles, and overall reproductive health through fertility tests, hormonal studies, blood tests, and consultation with a doctor. Knowing your hormone levels through test can guide you toward effective treatments and lifestyle changes.
This post dives into the basics of fertility hormone testing for men, what to expect, and how it can empower you in your family planning journey. Get ready to take control of your reproductive health and make informed decisions, men should test.
Key Takeaways
- Fertility hormone testing is essential for understanding reproductive health in men and can help identify potential issues affecting fertility.
- Individuals, including men, considering starting a family or experiencing difficulties conceiving should consult a healthcare provider about fertility hormone testing.
- Key hormones tested include Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Estradiol, Luteinizing Hormone (LH), and Progesterone in men, each playing a crucial role in the reproductive process.
- Understanding your hormone levels through test results can guide treatment options and improve chances of conception, making it important to discuss results with a specialist.
- Regular monitoring of fertility hormones is beneficial for men, especially for those with irregular cycles or a history of reproductive health issues, and should include a test.
- Educating yourself on the types of tests available for men can empower you to make informed decisions regarding your fertility journey.
What is Fertility Hormone Testing
Overview
Fertility hormone testing involves analyzing blood or urine samples. This testing helps identify hormonal issues affecting reproduction. The tests measure specific hormones in men that play a crucial role in fertility.
Key Hormones
Several hormones are assessed during fertility testing. These include estrogen, progesterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and test. Each hormone has a unique function in the reproductive process, test.
Estrogen regulates the menstrual cycle and prepares the uterus for pregnancy. Progesterone supports the early stages of pregnancy. LH triggers ovulation, while FSH stimulates egg production.
Testing Methods
Fertility tests can be done through blood draws or urine samples. Blood tests usually occur on specific days of the menstrual cycle. For example, testing FSH levels on day three of the cycle provides insights into ovarian reserve.
Urine tests can detect ovulation by measuring LH levels. A surge in LH indicates that ovulation is imminent. Home ovulation test kits use this method for tracking fertile windows.
Identifying Infertility Causes
Hormonal imbalances can lead to infertility. Fertility hormone testing helps determine these imbalances. For instance, low progesterone may indicate issues with ovulation. High prolactin levels can disrupt menstrual cycles and affect fertility, test results show.
Testing also identifies conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders. Both conditions can lead to irregular cycles and difficulty conceiving, test.
Treatment Options
Results from fertility tests guide treatment decisions. If hormonal issues are identified through tests, doctors may recommend lifestyle changes or medications. For example, weight loss can improve ovulatory function in women with PCOS, as shown by test results.
Medications like Clomid stimulate ovulation in women who do not regularly release eggs. Hormonal therapies can help balance estrogen and progesterone levels as well.
Timing and Frequency
Timing is critical for effective fertility hormone testing. Women should consult their healthcare provider to determine optimal testing days based on their cycle. Regular monitoring may be necessary if initial results indicate ongoing issues.
In some cases, men may also undergo fertility testing. Hormonal evaluations can assess testosterone levels and other factors influencing sperm production.
Purpose and Significance of Hormone Testing
Hormonal Evaluation
Hormone testing plays a crucial role in understanding fertility. It helps ensure proper ovulation, embryo implantation, and pregnancy maintenance. A hormone test can reveal whether the body produces adequate amounts of key hormones. These include estrogen, progesterone, and luteinizing hormone (LH). Each of these hormones is vital for reproductive health.
Hormonal evaluation studies often look at various hormonal levels throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle. This evaluation can pinpoint the right time for ovulation. It also identifies any abnormalities that may impact fertility. For men, testing can assess testosterone levels, which are essential for sperm production.
Identifying Imbalances
Testing can identify hormonal imbalances that affect fertility. Low thyroid function is one common issue. Hypothyroidism can lead to irregular menstrual cycles or even absence of periods. This condition affects ovulation and overall reproductive health.
High male hormone levels, such as testosterone, can also be problematic for women. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are linked to elevated androgen levels. PCOS can cause irregular periods and difficulty in getting pregnant. Hormonal studies provide insights into these conditions and help guide treatment options.
Treatment Guidance
Hormone testing serves as a foundation for developing treatment plans. After identifying specific hormonal issues, healthcare providers can recommend appropriate interventions. For example, if low thyroid function is detected, medication may be prescribed to restore normal levels.
In cases of high male hormones, lifestyle changes or medications might be suggested. These treatments aim to regulate hormone levels and improve fertility outcomes. By addressing these imbalances, individuals increase their chances of conception.
Monitoring Progress
Regular hormone tests allow for monitoring progress during treatment. Healthcare providers can adjust medications based on new test results. This ongoing assessment ensures that the chosen treatment remains effective.
Many couples find reassurance in knowing their hormone levels are being closely monitored. They gain insights into their reproductive health and understand what steps to take next.
Emotional Impact
Fertility challenges can be emotionally taxing. Knowing the purpose of hormone testing helps reduce anxiety about the unknowns of infertility. Understanding the specific hormonal factors at play provides clarity.
Couples often feel empowered by having information about their reproductive health. This knowledge allows them to make informed decisions regarding their family planning journey.
Who Should Consider Fertility Hormone Testing
Women’s Health
Women should consider fertility hormone testing if they experience irregular menstrual cycles. This can include cycles that are too long, too short, or skipped altogether. Such irregularities may indicate hormonal imbalances that affect ovulation.
Pelvic pain is another sign. Chronic pain can signal conditions like endometriosis, which impacts fertility. Unexplained weight changes can also play a role. Sudden weight gain or loss may disrupt hormone levels and menstrual cycles.
Couples Trying to Conceive
Couples facing challenges in getting pregnant should seek fertility hormone testing. Difficulty conceiving after one year of trying is a common guideline for seeking help. This is especially true for women over 35, where the timeline reduces to six months.
Hormonal issues can be a hidden cause of possible infertility issues. Testing can reveal problems with ovulation or other hormonal functions. Early detection allows couples to explore options sooner.
Men’s Fertility
Men should also consider hormone testing if they notice low sperm count or changes in sex drive. A low sperm count can significantly affect fertility. Hormonal imbalances often contribute to this issue.
Changes in libido can indicate underlying health problems as well. Low testosterone levels can result in decreased sexual interest and performance. Identifying these issues early can lead to effective treatments.
Importance of Testing
Testing plays a crucial role in understanding fertility health. It helps identify specific hormonal problems that may not be visible through regular check-ups. Knowing hormone levels can guide treatment options.
For women, tests often measure hormones like FSH, LH, and estradiol. For men, testosterone levels and other related hormones are evaluated. These tests provide valuable insights into reproductive health.
Next Steps After Testing
After receiving results, individuals should consult healthcare providers for guidance. They will explain what the results mean and discuss potential treatments. Options may include lifestyle changes, medications, or assisted reproductive technologies.
Understanding the outcomes of testing is essential for making informed decisions. Each case is unique, and tailored solutions are vital for success.
Types of Fertility Hormone Tests
FSH Testing
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) plays a key role in reproductive health. It helps control the menstrual cycle and stimulates the growth of eggs in ovaries. High levels of FSH can indicate reduced ovarian function. This test is often one of the common fertility tests performed on women, typically done on day 3 of their menstrual cycle.
Estradiol Testing
Estradiol is the primary form of estrogen in females. It prepares the uterine lining for potential pregnancy. Low estradiol levels may suggest issues with ovarian function. Doctors often check this hormone alongside FSH to gain a complete picture of fertility health.
LH Testing
Luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers ovulation and supports the menstrual cycle. Abnormal LH levels can affect fertility. A spike in LH indicates that ovulation is near, making it crucial for timing conception. Measuring LH is part of many fertility blood tests to assess reproductive hormone balance.
Progesterone Testing
Progesterone is essential for maintaining a pregnancy. After ovulation, progesterone prepares the uterus for implantation. Low levels may indicate problems with ovulation or early pregnancy loss. Testing progesterone usually occurs around day 21 of the menstrual cycle to confirm ovulation.
AMH Testing
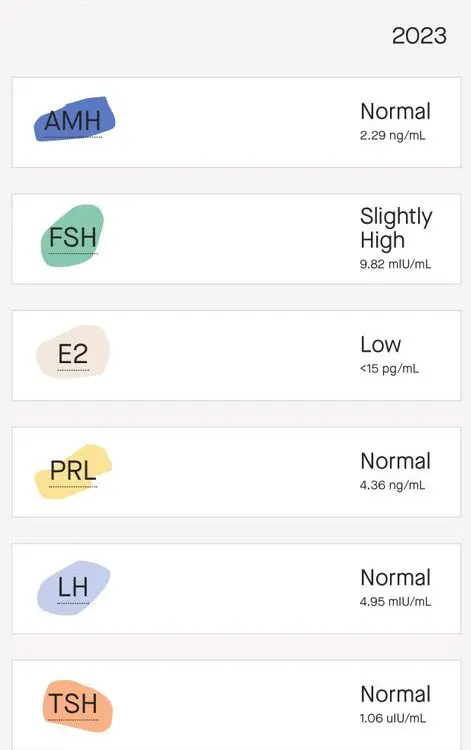
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) provides insight into ovarian reserve. It reflects the number of eggs left in the ovaries. Higher AMH levels suggest a better chance of successful conception. This test can be helpful for women considering fertility treatments or those worried about declining fertility as they age.
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Overview
FSH plays a vital role in female reproductive health. It regulates egg production and menstrual cycles in women. This hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland. It stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles, which are critical for ovulation.
FSH Test
The FSH test measures the level of this hormone in the blood. Doctors often recommend this test on day 3 of the menstrual cycle. This timing is crucial because it helps assess ovarian function at the start of the cycle.
Elevated levels of FSH on day 3 indicate potential issues with fertility. High FSH levels may suggest a reduced ovarian reserve. This means there are fewer viable eggs available for fertilization. Women with elevated FSH may face challenges in achieving pregnancy.
Ovarian Function
Ovarian function is essential for reproduction. FSH influences both the ovaries and the development of follicles. Each month, several follicles begin to mature under the influence of FSH. One follicle typically becomes dominant and releases an egg during ovulation.
If FSH levels are abnormal, it can affect menstrual cycles. Irregular cycles may occur when ovarian function is impaired. This can lead to difficulties in predicting ovulation and planning for conception.
Impact on Fertility
The relationship between FSH levels and fertility is significant. Elevated FSH levels can reduce the chances of live birth. This is particularly concerning for women trying to conceive later in life. As women age, their ovarian reserve naturally declines, leading to higher FSH levels.
Research indicates that high FSH levels can impact overall reproductive health. For example, studies show that women with elevated FSH have lower success rates with assisted reproductive technologies like IVF.
Estradiol
Role in Development
Estradiol is a key female hormone. It plays a vital role in the development of reproductive organs. This hormone is crucial for ovulation. Women need adequate estradiol levels for their menstrual cycle to function properly. The hormone also influences the development of breasts and other secondary sexual characteristics.
Estradiol levels fluctuate throughout a woman’s life. They peak during the reproductive years and decline with age. This decline can affect various aspects of health, including fertility.
Impact on Ovulation
Abnormal estradiol levels can disrupt ovulation. Low levels may lead to irregular cycles or anovulation, where no eggs are released. High levels can also signal issues, such as ovarian tumors or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
For women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF), estradiol levels are particularly important. Doctors monitor these levels closely. Proper estradiol values can improve the chances of successful IVF outcomes. If levels are not optimal, adjustments may be necessary before proceeding with treatment.
Importance for Uterine Lining
Estradiol is essential for maintaining the uterine lining. This lining thickens during the menstrual cycle under the influence of the hormone. A healthy lining is critical for implantation if pregnancy occurs.
Women with low estradiol levels may experience thinner uterine linings. This condition can hinder fertility efforts and increase the risk of miscarriage. Monitoring estradiol helps identify potential issues early on.
Testing Estradiol Levels
Doctors typically order estradiol tests on specific days of a woman’s cycle. The best time is usually around day 3 or day 21, depending on the purpose of the test.
Results from these tests provide insight into overall hormonal balance. Normal values vary based on age and sex. For premenopausal women, normal estradiol levels range from 30 to 400 picograms per milliliter (pg/mL). In contrast, postmenopausal women often have lower values, usually below 30 pg/mL.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Function
Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays a key role in the reproductive system. It is produced by the pituitary gland. This hormone triggers egg release during ovulation. It also prepares the uterus for a fertilized egg.
High levels of LH indicate that ovulation has occurred. This timing is crucial for those trying to conceive. Tracking LH levels helps determine the best days for intercourse. Many women use ovulation predictor kits for this purpose.
Testing
LH testing can be done through a simple blood test. Doctors often recommend this test when assessing fertility issues. The results can help identify hormonal imbalances affecting fertility.
A normal LH level varies throughout the menstrual cycle. Levels are typically lower in the follicular phase and peak just before ovulation. Understanding these patterns aids in recognizing potential problems.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can affect many aspects of health, including fertility. High or low LH levels may signal underlying conditions. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to elevated LH levels.
Women with PCOS often experience irregular periods and difficulty conceiving. Low LH levels can also indicate issues with the pituitary or thyroid glands. These glands play vital roles in hormone production and regulation.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing signs of hormonal imbalance is important. Irregular menstrual cycles, weight changes, and mood swings may occur. Women should consult healthcare providers if they notice these symptoms.
Blood tests can provide insights into hormone levels, including TSH, LH, and AMH. Testing these hormones helps assess ovarian function and egg reserve.
Importance of LH
LH is essential for reproductive health. It influences multiple organs involved in reproduction. Monitoring LH levels provides valuable information about fertility status.
Doctors often look at LH in conjunction with other hormones like estradiol and progesterone. This comprehensive approach helps form a clearer picture of a woman’s hormonal health.
Progesterone
Hormone Function
Progesterone plays a vital role in the menstrual cycle. It prepares the uterus for a fertilized egg after ovulation. This hormone thickens the endometrium, making it suitable for implantation.
Peak levels of progesterone occur about one week after ovulation. This surge helps maintain the uterine lining. Without adequate progesterone, the body cannot sustain a pregnancy.
Testing Methods
The serum progesterone test measures the amount of this hormone in the blood. Physicians often recommend this test during specific times in the menstrual cycle. A luteal serum progesterone test is common for assessing ovulation and fertility.
Urine tests can also detect progesterone levels but are less precise than blood tests. These tests help identify low progesterone conditions, which may affect fertility.
Low Progesterone Effects
Low progesterone can lead to various symptoms. Women may experience irregular menstrual cycles or heavy bleeding. Some may face difficulties with implantation or maintaining a pregnancy.
This condition can result from several factors, including stress, poor nutrition, or certain medications. It is crucial for women experiencing these symptoms to consult a physician for proper evaluation.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for low progesterone vary based on individual needs. Hormonal medications are common to boost progesterone levels. These treatments help restore balance and support early pregnancy.
Lifestyle changes can also aid in managing progesterone levels. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports hormone production. Regular exercise reduces stress, which can positively impact hormone balance.
Importance in Pregnancy
During early pregnancy, progesterone is crucial for sustaining the developing embryo. It prevents contractions of the uterus that could lead to miscarriage. The hormone also supports blood flow to the uterus, helping nourish the fetus.
Monitoring progesterone levels during pregnancy is important for both mother and baby. Physicians often check these levels to ensure they are within a healthy range. This monitoring helps identify any potential complications early on.
Other Hormones in Fertility Testing
Anti-Müllerian Hormone
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) plays a crucial role in female fertility testing. This hormone indicates ovarian function and helps assess the ovarian reserve. Higher AMH levels suggest a greater number of available eggs.
Doctors often measure AMH through blood tests. These tests typically occur on any day of the menstrual cycle. A low AMH level can signal reduced fertility potential. This is important for women considering pregnancy, especially as they age.
Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones also affect overall fertility. The thyroid regulates metabolism and energy levels in the body. An imbalance can lead to fertility problems.
Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, can cause irregular menstrual cycles and affect ovulation. Women with this condition may experience female infertility. Conversely, hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, can also disrupt reproductive health. Thyroid hormone levels should be checked during infertility diagnosis.
Prolactin Levels
Prolactin is another significant hormone in fertility testing. This hormone primarily controls milk production after childbirth. However, elevated prolactin levels can impact menstrual cycles and ovulation.
High levels of prolactin can lead to fertility trouble for both men and women. In women, it may cause irregular periods or even amenorrhea (absence of menstruation). In men, high prolactin can lead to decreased testosterone levels and lower sperm production.
Doctors often check prolactin levels through blood tests if patients report irregular cycles or other fertility issues. Addressing high prolactin levels can improve chances of conceiving.
Other Important Hormones
Several hormones contribute to fertility beyond those already mentioned. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) are vital in regulating the menstrual cycle and stimulating ovarian hormone production.
LH triggers ovulation while FSH promotes egg maturation. Abnormal levels of these hormones can indicate underlying fertility problems.
Androgens, often labeled as male hormones, are present in both genders. Elevated androgen levels in women can lead to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which affects ovulation.
Hormone test results provide essential insights into reproductive health. Understanding these important hormones helps tailor treatment options for individuals facing infertility challenges.
Closing Thoughts
Fertility hormone testing is a vital step for anyone looking to understand their reproductive health. Knowing your hormone levels can guide your journey, whether you’re planning a family or facing challenges. Each test provides valuable insights into your unique situation, empowering you to make informed decisions.
Don’t wait for uncertainty to take over. If you think fertility hormone testing might be right for you, reach out to a healthcare professional today. They can help you navigate the process and interpret your results. Take charge of your fertility journey—your future self will thank you for it!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is fertility hormone testing?
Fertility hormone testing measures key hormones affecting reproductive health. It helps identify imbalances that may impact fertility, guiding treatment options for individuals or couples trying to conceive.
Why is fertility hormone testing important?
This testing is crucial for diagnosing potential fertility issues. It provides insights into hormonal levels, helping healthcare providers tailor treatments and improve chances of conception.
Who should consider fertility hormone testing?
Individuals experiencing difficulty conceiving, irregular menstrual cycles, or unexplained infertility should consider this testing. It’s also beneficial for those with a history of hormonal disorders.
What types of fertility hormone tests are available?
Common tests include Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Estradiol, Luteinizing Hormone (LH), and Progesterone. Each test assesses different aspects of reproductive health.
When should I get tested for fertility hormones?
Testing is typically recommended during specific phases of the menstrual cycle. Consult your healthcare provider to determine the best timing based on your individual situation.
Can lifestyle changes affect fertility hormone levels?
Yes, lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and stress management can influence hormone levels. Making positive changes may enhance overall reproductive health and fertility.
How do I interpret my fertility hormone test results?
Interpreting results requires professional guidance. A healthcare provider will explain what the levels mean in relation to your fertility goals and recommend any necessary next steps.
