Posted August 13, 2024 in Fertility Blog & Information
18 minute read

Male infertility causes, such as impaired sperm, low sperm production, sperm defects, and poor semen quality, and treatments are crucial topics for many couples. Understanding the various factors that contribute to male infertility, such as feelings in symptomatic hypogonadal men, watery semen, and ejaculation, can empower individuals to seek help. Common causes include hormonal imbalances, genetic issues, and lifestyle choices like smoking or obesity, which can contribute to possible infertility and affect male infertility patients, impacting male infertility overall and the male infertility factor. Treatments range from medications to advanced assisted reproductive technologies. Each case, including those related to male infertility issues, is unique, highlighting the importance of personalized solutions that consider symptoms and feelings. Knowledge is power, and addressing these feelings and issues head-on can lead to successful outcomes. With the right information and support, many men can overcome these challenges and achieve their dreams of fatherhood.
Key Takeaways
- Male infertility can affect anyone and is influenced by various medical, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Understanding these can help you identify risks.
- Look out for signs of unhealthy sperm, such as low libido or erectile dysfunction, which may indicate underlying issues.
- Common medical causes include hormonal imbalances and genetic conditions, while lifestyle factors like smoking and obesity can also play a significant role.
- Diagnosis of male infertility often involves semen analysis and hormone testing; don’t hesitate to seek professional help if you notice concerning symptoms.
- Treatment options vary from lifestyle changes to medical interventions like hormone therapy or assisted reproductive technologies, so explore what suits your situation best.
- If you’ve been trying to conceive for over a year without success, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Overview of Male Infertility
Definition
Male infertility is defined as the inability to cause pregnancy in a fertile female. This condition can arise from various factors affecting sperm production or function.
Prevalence
Approximately 7% of all men experience infertility issues. This statistic highlights how common male infertility is among the population. It is important to recognize that infertility can affect any man, regardless of age or background.
Causes
Many factors contribute to male infertility. Medical issues often play a significant role. Conditions like diabetes, hormonal imbalances, and infections can impact fertility. Genetic factors, such as chromosomal abnormalities, also contribute to this issue. Environmental factors should not be overlooked either. Exposure to toxins, heavy metals, and radiation can negatively affect sperm health.
Lifestyle choices can further influence male fertility. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are known to reduce sperm quality. Obesity has also been linked to infertility in men. These lifestyle factors can lead to lower testosterone levels and poor semen production.
Evaluation Process
The male infertility evaluation typically begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Doctors may ask questions about sexual history and any previous health issues. This helps identify potential causes of infertility.
Semen analyses are crucial during evaluations. These tests measure various parameters, including sperm count, motility, and morphology. A normal semen analysis shows at least 15 million sperm per milliliter. Low sperm counts can indicate fertility problems.
Additional tests might include hormone level assessments and genetic testing. Hormonal evaluations check for imbalances that could affect sperm production. Genetic tests can reveal conditions like Klinefelter syndrome, which impacts fertility.
Treatment Options
Treatment for male infertility varies based on the underlying cause. In some cases, lifestyle changes can improve fertility outcomes. Weight loss, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol intake may enhance sperm quality.
Medical treatments are available for specific conditions. Hormonal therapies can help restore balance if hormonal issues exist. Antibiotics may treat infections affecting fertility.
Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) offer options for couples struggling with infertility. Techniques like in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) can aid in conception. These methods allow doctors to bypass certain fertility barriers.
Who is Affected?
Age Factors
Men of all ages can experience infertility. However, the likelihood increases with age. Research shows that infertility is more common in men over 40 years old. As men age, sperm quality often declines. This decline can lead to difficulties in conceiving a child.
Younger men can also face fertility issues. Yet, older men are generally at higher risk. Hormonal changes and health problems often contribute to this increased risk.
Body Weight
A high body mass index (BMI) plays a significant role in male infertility. Men with obesity are more likely to face fertility challenges. Studies indicate that excess weight can affect hormone levels. This change leads to reduced sperm production and quality.
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reproductive health. Losing even a small amount of weight may improve fertility outcomes. Men should consider regular exercise and a balanced diet to manage their weight effectively.
Medical History
Certain medical conditions increase the risk of male infertility. Men who have a history of undescended testicles face greater challenges in fertility. This condition occurs when one or both testicles do not descend into the scrotum before birth.
Varicoceles also contribute to infertility risks. Varicoceles are enlarged veins within the scrotum. They can affect sperm production and quality by raising testicular temperature. Men with this condition should seek medical evaluation if they have concerns about fertility.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also impact male fertility. Exposure to toxins, chemicals, and heavy metals can reduce sperm quality. Common sources include pesticides, industrial chemicals, and air pollution.
Lifestyle choices play a critical role as well. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption negatively affect sperm parameters. Men should be aware of these influences on their reproductive health.
Genetic Factors
Genetics may also contribute to male infertility issues. Certain genetic disorders can impair sperm production or function. Klinefelter syndrome is one example where males have an extra X chromosome, leading to lower testosterone levels and reduced fertility.
Men with family histories of infertility should consult healthcare providers for guidance. Genetic testing may provide insights into potential fertility issues.
Signs of Unhealthy Sperm
Malformed Sperm
Malformed sperm is a key indicator of unhealthy sperm. These abnormalities can affect the shape and structure of the sperm. Normal sperm has a smooth oval head and a long tail. However, malformed sperm may have irregular shapes. Some might have two tails or misshapen heads. Such defects can hinder the sperm’s ability to reach and fertilize an egg.
Abnormal sperm production leads to these malformations. Factors like environmental toxins, poor diet, and certain medical conditions contribute to this issue. A semen analysis can reveal these abnormalities. This test measures the sperm characteristics in a sample.
Low Sperm Count
Low sperm count, known as oligospermia, is another significant sign of unhealthy sperm. A normal sperm count ranges from 15 million to over 200 million sperm per milliliter of semen. Counts below this range indicate potential fertility issues.
Oligospermia can arise from various factors. Hormonal imbalances, genetic disorders, and lifestyle choices play a role. Men who smoke or consume excessive alcohol often face this challenge. Stress and obesity also impact sperm count negatively.
A semen analysis helps determine if low sperm count exists. The results can guide further evaluation and treatment options.
Absence of Sperm
The absence of sperm in semen, termed azoospermia, is a critical indicator of male infertility. This condition means no sperm is present in the ejaculate. It can stem from blockage in the reproductive system or hormonal issues.
Azoospermia affects about 1% of men overall but increases in cases of infertility. Men with this condition may still produce testosterone but lack viable sperm for reproduction.
Diagnosis requires careful examination through a semen analysis. If azoospermia is confirmed, further tests are necessary to identify the underlying cause. Treatments may include surgery to remove blockages or hormone therapy.
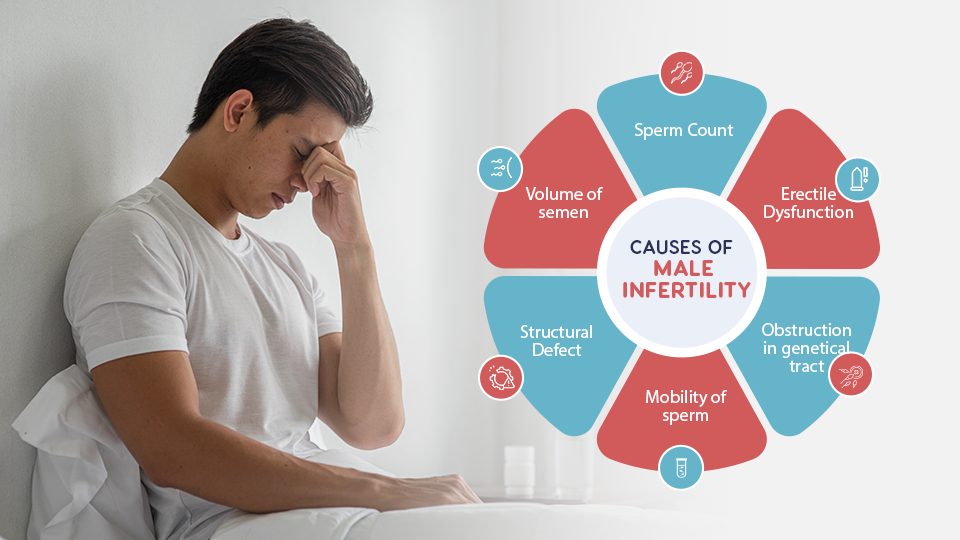
Causes of Male Infertility
Genetic Disorders
Genetic issues can lead to male infertility problems. Conditions like Klinefelter syndrome affect the male chromosome structure. This syndrome results in lower testosterone levels and poor sperm production. Myotonic dystrophy is another genetic disorder that can impact fertility. It causes muscle weakness and may also interfere with sperm quality.
Infections
Infections play a significant role in male infertility issues. Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis, often caused by infections. Orchitis, an inflammation of the testicles, can also occur due to viral or bacterial infections. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea and HIV can severely affect male fertility. They may cause scarring or blockages, leading to low sperm count or poor sperm function.
Testicular Trauma
Testicular trauma can result from injuries during sports or accidents. Damage to the testicles can lead to male fertility problems. Even minor injuries may disrupt normal hormone levels or sperm production. Men who experience such trauma should seek medical advice promptly.
Varicoceles
Swollen veins in the testicles, known as varicoceles, are common among men with fertility issues. These veins can increase temperature in the testicular area, affecting sperm production. Varicoceles are linked to male factor infertility and may be found in 15% of all men but are more prevalent in those facing fertility challenges.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can also contribute to male infertility factors. Low testosterone levels may hinder sperm production and overall reproductive health. Other hormones, including luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), must also be balanced for optimal fertility.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices can impact male fertility as well. Smoking and excessive alcohol use reduce sperm count and quality. Obesity is another factor that affects hormone levels and sperm production negatively. Men should consider adopting healthier habits to improve their chances of conception.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to environmental toxins may lead to male subfertility. Chemicals such as pesticides and heavy metals have been linked to reduced sperm quality and production. Limiting exposure to these substances can help protect reproductive health.
Idiopathic Infertility
etimes, no clear cause is found for male infertility. This condition is termed idiopathic male infertility. Despite thorough testing, doctors cannot identify specific issues in these cases. This unexplained infertility can be frustrating for couples trying to conceive.
Medical Causes
Diabetes
Diabetes can significantly affect male fertility. High blood sugar levels may damage nerves and blood vessels. This can lead to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection. Diabetes can disrupt hormone levels, which may reduce sperm production.
Men with diabetes often face emotional challenges as well. Feelings of anxiety and frustration can arise from infertility issues. Managing diabetes requires a balanced diet, regular exercise, and medication. These lifestyle changes can improve overall health and potentially enhance fertility.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases can also impact male fertility. Conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis may cause the body to attack its own cells, including sperm cells. This can lead to lower sperm quality or quantity.
Symptoms of autoimmune diseases vary widely. Some men may experience fatigue or joint pain. Others might notice changes in libido or sexual function. Treatment for these conditions often includes immunosuppressive medications. These drugs help manage symptoms but may have side effects that affect fertility.
Cancer Treatments
Cancer treatments are another significant cause of male infertility. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy target rapidly dividing cells, which include sperm cells. These treatments can drastically reduce sperm count and motility.
Surgical removal of testicles, known as orchiectomy, directly impacts hormone production and sperm creation. Men undergoing these treatments often feel overwhelmed by the emotional toll. It is essential for them to discuss fertility preservation options before starting treatment.
Hormonal Disorders
Hormonal disorders can disrupt the balance of hormones necessary for sperm production. The hypothalamus and pituitary glands play crucial roles in regulating these hormones. Issues in these areas may lead to low testosterone levels.
Low testosterone can result in decreased libido and reduced sperm production. Symptoms may include fatigue, weight gain, and mood changes. Treatment options include hormone replacement therapy or medications to stimulate hormone production.
Vitamins and Minerals
Nutritional deficiencies can also contribute to male infertility. Essential vitamins and minerals support overall reproductive health. For example, zinc is crucial for testosterone production and sperm development.
Men should ensure they consume a balanced diet rich in these nutrients. Foods like nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables provide vital vitamins for reproductive health. Supplements may be beneficial if dietary intake is insufficient.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Radiation Exposure
Exposure to radiation can harm male fertility. Studies show that even low levels of radiation can affect sperm quality. This includes exposure from medical treatments like X-rays or radiation therapy.
Environmental toxins also play a significant role. Chemicals like lead, mercury, and pesticides are harmful. They can disrupt hormonal balance and reduce sperm production. Men working in industries with these substances face higher infertility risks.
Substance Use
Tobacco use is one of the major contributors to male infertility. Smoking reduces sperm count and motility. It also damages the genetic material in sperm. Research indicates that men who smoke may have a harder time fathering children.
Marijuana use has similar effects. Studies suggest it can lower testosterone levels and impair sperm function. Regular users may experience reduced fertility over time.
Alcohol consumption impacts fertility as well. Heavy drinking can lead to hormonal imbalances. This affects sperm production and overall reproductive health. Limiting alcohol intake can improve fertility chances.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for fertility. Obesity can lead to hormonal changes that negatively affect sperm production. Men with a BMI over 30 often experience lower fertility rates.
Weight loss can improve fertility outcomes. Losing just 5-10% of body weight may enhance sperm quality and hormone levels.
Heat Exposure
Heat exposure significantly affects testicle temperature. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can damage sperm production. Activities like using saunas or hot tubs raise testicle temperature.
Men who spend long hours in tight clothing or sit for extended periods may face similar issues. Wheelchair users, for instance, might experience increased heat around the genital area, leading to infertility concerns.
Partner Factors
A partner’s health also influences male fertility. Women with certain medical conditions may struggle to conceive, impacting their partner’s perception of their own fertility status. Stress from these situations can further complicate matters.
Healthy relationships are essential for emotional support during this journey. Open communication about concerns helps couples navigate challenges together.
Diagnosis Methods
Semen Analysis
Semen analysis is the first step in diagnosing male infertility. This test evaluates sperm count and quality. A sample of semen is collected and examined under a microscope.
Doctors check for several factors during this analysis. They look at the number of sperm present. A normal sperm count ranges from 15 million to over 200 million sperm per milliliter. They also assess sperm motility, which is how well the sperm move. Healthy sperm should swim forward effectively.
Morphology is another important aspect. This refers to the shape and structure of the sperm. Abnormal shapes can affect the ability to fertilize an egg. Semen analysis provides crucial information about a man’s fertility potential.
Hormone Testing
Hormone testing plays a vital role in diagnosing male infertility as well. It checks for imbalances that can impact fertility. Doctors typically measure levels of hormones such as testosterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
Low testosterone can lead to reduced sperm production. High levels of LH and FSH may indicate problems with the testicles or pituitary gland. These tests help identify underlying hormonal issues that might contribute to infertility.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is another method used in diagnosis. It helps identify potential inherited conditions affecting fertility. Conditions like Klinefelter syndrome can lead to low testosterone and reduced sperm production.
Doctors may recommend genetic tests if there are abnormal results from semen analysis or hormone testing. These tests can reveal chromosomal abnormalities or mutations that could hinder fertility.
Importance of Comprehensive Diagnosis
A comprehensive approach is essential when diagnosing male infertility. Factors such as environmental influences and lifestyle choices also play a significant role. For example, exposure to toxins or poor diet can worsen fertility issues.
Understanding all aspects of male fertility allows doctors to create effective treatment plans. Combining different diagnostic methods leads to better outcomes for men facing infertility challenges.
Treatment Options
Medication
Hormonal imbalances often cause male infertility. Medications can help restore proper hormone levels. For example, testosterone replacement therapy can be effective for men with low testosterone. This treatment aims to improve libido and sperm production.
Another option is clomiphene citrate. This medication stimulates the pituitary gland. It increases the production of hormones that help produce sperm. Studies show it can improve fertility in some men.
Medications like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) can aid in treatment. hCG mimics luteinizing hormone, which helps stimulate testosterone production. These medications are vital for addressing hormonal issues.
Surgical Interventions
e men face structural problems affecting fertility. Varicoceles are enlarged veins in the scrotum that can hinder sperm production. Surgery to repair varicoceles can improve fertility rates significantly. A study from 2018 found that about 60% of men who had this surgery achieved pregnancy within a year.
Blockages in the reproductive tract can also prevent sperm from reaching the semen. Surgical procedures can remove these blockages. Techniques like vasectomy reversal or epididymal sperm aspiration can restore fertility.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) provide additional options for couples facing infertility. In vitro fertilization (IVF) is one of the most common methods. During IVF, doctors retrieve eggs from the female partner and fertilize them with sperm in a lab. The fertilized eggs develop into embryos before being implanted back into the uterus.
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is another technique used during IVF. This method involves injecting a single sperm directly into an egg. ICSI is particularly helpful for men with severe sperm quality issues or low sperm count.
These technologies have transformed how couples approach infertility. Success rates vary based on several factors, including age and health conditions. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 30% of IVF cycles result in live births.
When to Seek Help
Unsuccessful Attempts
Men should seek help after one year of unsuccessful attempts to conceive. This timeline is crucial for identifying potential issues. Many couples may not realize that infertility can stem from male factors. If a couple has been trying for a year without success, it’s time to consult a healthcare provider.
Known Risk Factors
Consulting a specialist is important if there are known risk factors or medical conditions. Certain health issues can affect fertility. Conditions like diabetes, hormonal imbalances, or previous surgeries can play a role in male infertility. Men with these conditions should not wait too long to seek help. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes.
Age Considerations
Men over 40 should consider early consultation. Fertility naturally declines with age. Research shows that men in this age group may have lower sperm quality and quantity. Those with a history of reproductive issues also need to act sooner rather than later. Delaying consultation can result in missed opportunities for effective treatment.
Symptoms to Watch For
Men should be aware of symptoms that indicate the need for help. Issues like erectile dysfunction, low libido, or changes in sexual function can signal underlying problems. Physical signs such as swelling in the testicular area or pain also warrant immediate attention. Recognizing these signs early can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment.
Partner’s Health
The health of a partner is also relevant when seeking help. Male infertility often involves both partners’ reproductive health. If the female partner has had known fertility issues, men should seek evaluation sooner. Addressing both partners’ health can improve chances of conception.
Importance of Evaluation
A thorough evaluation is key in addressing male infertility. Specialists may recommend tests such as semen analysis, hormone testing, or genetic screening. These tests provide valuable insights into fertility status and guide treatment options.
Emotional Impact
The emotional toll of infertility is significant for many men. Feelings of inadequacy or frustration are common when facing challenges in conceiving. Seeking help can alleviate some of this stress by providing answers and potential solutions.
Final Remarks
Male infertility is a complex issue that affects many men today. Understanding the causes, signs, and treatment options is crucial for you and your partner. From medical conditions to lifestyle choices, various factors can impact sperm health. Early diagnosis can lead to effective treatments and better outcomes.
Don’t hesitate to seek help if you notice any signs of infertility. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide clarity and open doors to solutions tailored for you. Knowledge is power—take charge of your reproductive health today. Your journey towards fatherhood may just be a conversation away.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of male infertility?
Common causes include hormonal imbalances, genetic factors, medical conditions like diabetes, and environmental influences such as exposure to toxins.
How can lifestyle choices affect male fertility?
Lifestyle choices like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of exercise can negatively impact sperm quality and fertility.
What are the signs of unhealthy sperm?
Signs of unhealthy sperm may include low sperm count, abnormal shape, poor motility, or difficulty achieving pregnancy after a year of trying.
How is male infertility diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, semen analysis, hormone testing, and sometimes imaging tests to assess reproductive organs.
What treatment options are available for male infertility?
Treatment options may include lifestyle changes, medications, surgery for blockages, assisted reproductive technologies like IVF, or using donor sperm.
When should I seek help for infertility issues?
Seek help after one year of unsuccessful attempts to conceive if you’re under 35. For those over 35, consult a specialist after six months.
Can male infertility be reversed?
In some cases, yes. Addressing underlying medical conditions or making lifestyle changes can improve fertility. However, it depends on individual circumstances.
